16.2. What is a Terminal?¶
16.2.1. GUIs and CLIs¶
Most of the time when we use our computers and smartphones, we do so through a graphical user interface, or GUI for short. A GUI is a system designed to use icons and visual tools to manage tasks. Creating a new folder, running programs, and moving or deleting files are all done by selecting menu items or clicking icons on the screen.
Three examples of graphical user interfaces: a folder navigation box, a desktop, and a smartphone home screen.¶
Programmers often use another kind of interface, called the command line. A CLI, or command line interface, uses text to give the computer instructions instead of dragging and dropping icons.
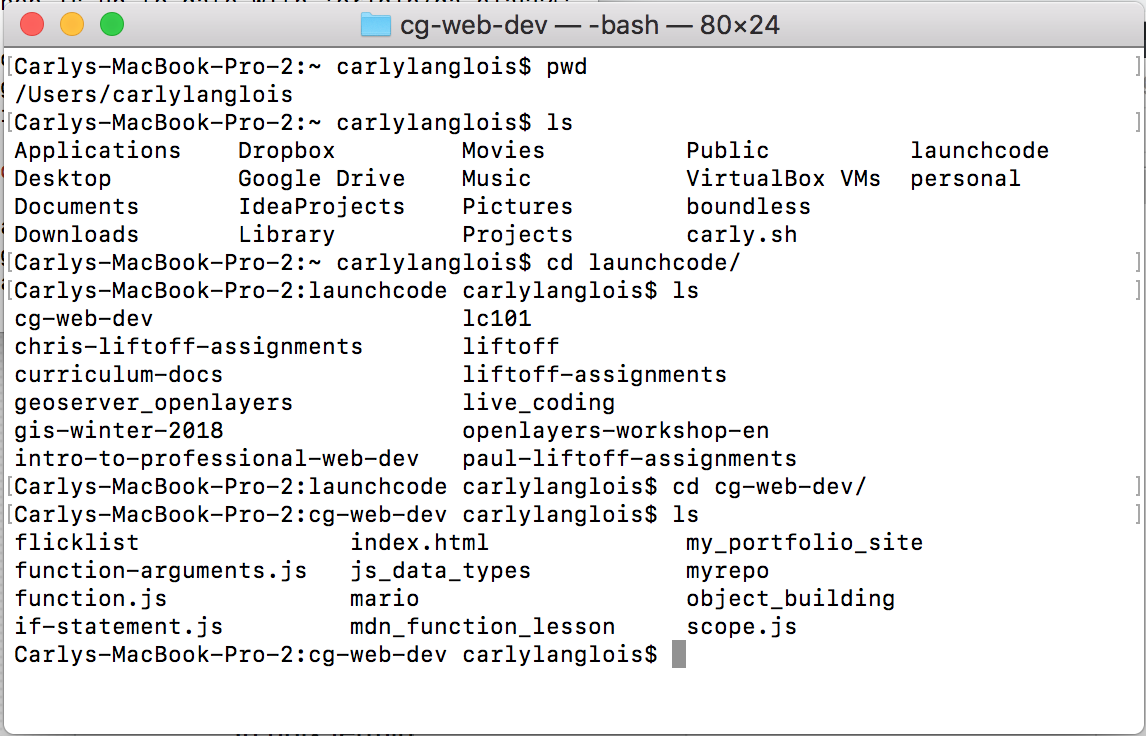
A CLI showing commands for navigating a file tree.¶
The application responsible for running a CLI is called a terminal. The program that interprets the commands is called the shell.
Note
The terms command line, terminal, and shell are often used interchangeably.
16.2.2. Why Use the Terminal?¶
Both GUIs and CLIs allow us to access and modify files on our device. Most of us are familiar with GUIs, and they are very user-friendly. However, using a CLI makes some tasks easier or more efficient. We need to be familiar with both types of interfaces.
In the terminal, we will be able to:
Quickly move through our computer’s file structure.
Make new files and folders.
Move or delete files and folders.
Install software.
Open applications.
Run the programs we code.
16.2.3. Launch the Terminal¶
As you read the next few sections, it helps to have the terminal open. That way, you can work through the examples and get used to the CLI. Follow the instructions below to launch the application.
While we cannot predict the setup on your personal device, these guides should point you in the right direction.
16.2.3.1. Mac Users¶
In the Finder, navigate to the Applications folder. Find the icon by opening the window for your hard drive. The folder icon may also appear in the dock.
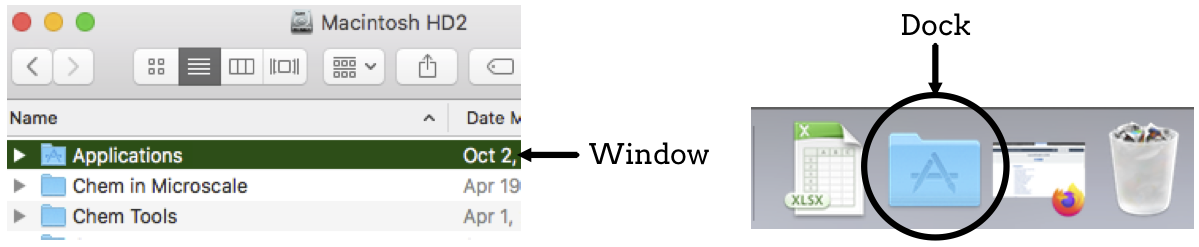
Double-click the hard drive icon to find the Applications folder, or check the dock.¶
Inside the Applications folder, find the Utilities folder.
Open the Utilities folder to find the Terminal application!
Another way to locate the application is to run a search in the Finder for “Terminal”.
Tip
Once you locate the Terminal application, you can add it to the dock! Just drag and drop the icon into the dock. This lets you quickly launch the program the next time you need it.
16.2.3.2. Windows Users¶
The terminal application we will use in this course is called Git Bash.
Open the Start menu by clicking on the Windows icon found in the lower left corner of the screen.
From the list of items that pops up, select Git Bash to open the CLI.
If the list is long, try typing “Git Bash” into the Start menu search bar. This narrows down the options displayed.
Tip
To put an icon for the CLI on your desktop, right-click on the Git Bash name in the start menu. Select the Add Shortcut To Desktop option. Another option pins GitBash to the taskbar.
16.2.3.3. Chromebook Users¶
Note
If you use a virtual desktop for this class, login to that service. Follow the instructions for Mac or Windows, depending on the OS used for the desktop.
Expand the dock at the bottom of your Chromebook desktop.
Find Terminal in the list of icons that appears. The application is probably inside the Linux apps subfolder. It’s icon shows the
>_symbols.
Click on the icon to launch the program.
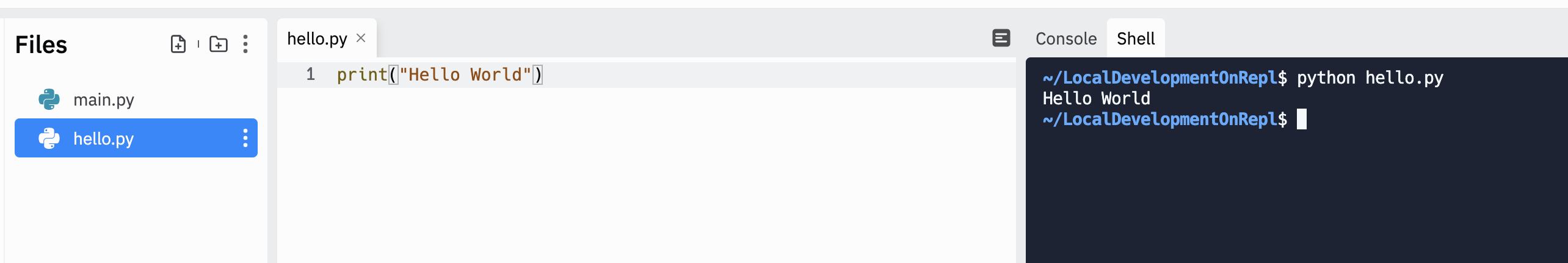
16.2.3.4. Replit Users¶
Note
If you use Replit for this class, login to your account.
Create a new python repl.
Click on the shell tab.
To run a file, at the prompt type python filename