20.8. Form Validation with HTML5¶
On the Text Inputs page, we looked at
client-side validation. By changing the type attribute in the <input>
tag, we make the browser perform a quick check of the data entered into a
field. Types like number, email, date, etc. compare the data from
an input box to a particular format. However, these checks do NOT prevent a
user from leaving an input blank.
The required attribute prevents form submission if the user skips one or
more of the input fields. It flags any input that returns the empty string
("") as its value.
required lets us place an emphasis on the most important information we
need to collect from a form.
Example
The Name and Student ID fields are necessary, but Favorite Color
can be left blank.
1 2 3 | <input type="text" name="name" placeholder="Enter your full name." required/>
<input type="password" name="id_num" required/>
<input type="text" name="fav_color"/>
|
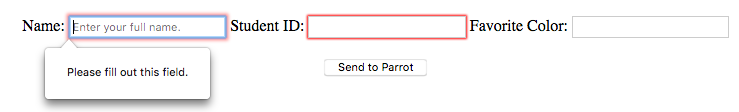
After trying to submit the form, red borders flag the empty, required fields.¶
The required attribute also works for non-text inputs as well.
Radio buttons: Only one
requiredattribute is needed for the group. This group consists of allinputelements that share the samenameattribute.1 2 3
<label><input type="radio" name="color" value="red" required/> Red</label><br> <label><input type="radio" name="color" value="green" /> Green</label><br> <label><input type="radio" name="color" value="blue" /> Blue</label>
Select element: Place the
requiredattribute inside the<select>tag. Also, one of the<option>tags must includeselectedand assign the empty string to thevalueattribute.1 2 3 4 5
<select name="color" required> <option value="" selected>Choose a color:</option> <option value="red">Red</option> <!-- etc. --> </select>
Checkboxes: If we need the user to click a specific checkbox, then the
requiredattribute works well. This would be something like those I agree to the terms and conditions statements we need to click before installing new software or creating an online account.
Note that HTML5 currently does NOT support using required on a group of
checkboxes, even if they share the same name. If we want to make sure the
user clicked at least one checkbox option, we need to use a different
validation method.
Server-side validation refers to actions that happen after a form is submitted. When the server receives a request containing form data, it runs code to check that data. If any information is missing or in the wrong format, the server sends a response that flags the errors.
Client-side validation takes place before contacting the server. The browser prevents submission if it finds a problem inside the form. Server-side validation occurs afterwards, and it gives developers much more control over how to check the data. Good developers combine both validation methods to build strong webpages. We will study server-side validation in the next few chapters.
20.8.1. Check Your Understanding¶
Question
When should we include form validation in our code?
- Anytime the user enters a password.
- Anytime the user needs to provide required data.
- Anytime the data in an input field needs to follow a specific format.
- Anytime we build a form.
- All of the above.
Question
A user fills out a form with their login information and clicks Submit. They receive an error message pointing out that they entered an incorrect password for their account. This is an example of:
- client-side validation
- sever-side validation
