24.5. Database Practice¶
On this page, we will add rows to the students table and then learn how to
access and view that data from our Python program.
24.5.1. Add New Entries¶
Code along with this video as we add new rows to the students table.
Key points:
Use the INSERT INTO query to add a new row.
Notice the
(?, ?, ?)at the end of the query string. The question marks serve as placeholders for the values we want to save in the new row.We indicate those values with arguments inside the
.execute()method.Note that we do not need to include a primary key value when we add a row. This process is automatic with SQLite.
Use the
.commit()method to finish the process.
Final code from the video:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | import sqlite3
# Connect to the practice.db database:
database = sqlite3.connect('practice.db')
cursor = database.cursor()
# Create the 'students' table if not already there:
sql_query = "CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS students (last_name TEXT, first_name TEXT, grad_year INT)"
cursor.execute(sql_query)
# Collect values for the 3 table columns:
last_name = input("Enter your last name: ").capitalize()
first_name = input("Enter your first name: ").capitalize()
grad_year = int(input("Enter your graduation year: "))
# Add a new row to the 'students' table, them commit.
sql_query = "INSERT INTO students (last_name, first_name, grad_year) VALUES (?, ?, ?)"
cursor.execute(sql_query, (last_name, first_name, grad_year))
database.commit()
|
24.5.1.1. Viewing a Table in VS Code¶
To view the data stored in practice.db, we need to add an extension to
Visual Studio Code. Follow along with this video to make the update:
Summary:
Click the extensions button in VS Code. Enter
SQLitein the search bar, then select and install the extension byalexcvzz.
It only takes about 3 clicks to install the SQLite extension.¶
Return to the file tree. Right-click on
practice.dband select Open Database. At the bottom-left of the VS Code workspace, open the SQLITE EXPLORER tab. Expandpractice.db, then click on the Play button next to thestudentstable.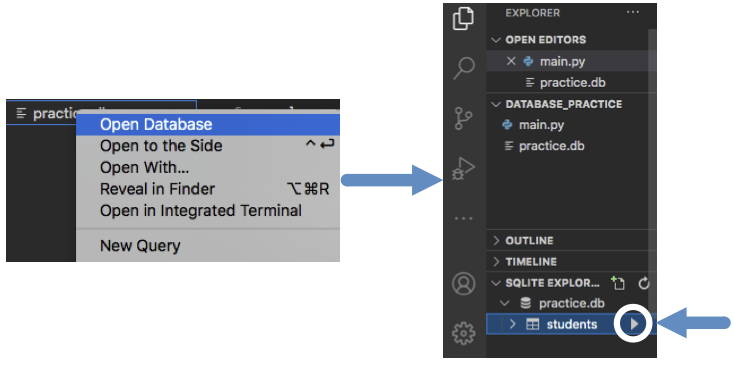
Click the Play arrow to view the contents of the student table.¶
24.5.2. Retrieve Data From Table¶
Code along with this video as we access the information in the database and
display it in the console. We will reuse the main.py and practice.db
files. However, we no longer need to CREATE the table or INSERT more rows. To
avoid some runtime and logic errors, be sure to comment out the statements
in lines 6 - 15.
We will add new code below those commands.
Key points:
Use the SELECT query to read specific columns from a table.
The query returns a cursor object, which can be assigned to a variable.
The order of the columns in the
SELECTstatement determines the order of the data in the results.By default,
SELECTreturns data from all rows in the table. Adding theWHEREkeyword to the query lets us filter the results.WHEREacts like anifstatement.Use the
list()function to change the cursor object to a list. This allows us to easily manipulate the returned data.
Sample code:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 | import sqlite3
database = sqlite3.connect('practice.db')
cursor = database.cursor()
# Choose which columns and rows to return from the 'students' table.
sql_query = "SELECT last_name, grad_year FROM students WHERE grad_year < 2010"
# Run the SQL query and assign the returned values to 'results'.
results = list(cursor.execute(sql_query))
results.sort()
print("Last Name\tGraduation Year")
for result in results:
# Each entry in 'results' contains 2 values, result[0] and result[1].
row = f"{result[0]}\t\t{result[1]}"
print(row)
|
24.5.3. Check Your Understanding¶
Question
Which SQL keyword adds new rows to a table?
-
SELECT -
UPDATE -
INSERT -
CREATE
Question
Which SQL query shows the shortcut for returning data from all columns of a table?
-
SELECT * FROM table_name -
SELECT all FROM table_name -
SELECT columns FROM table_name -
SELECT FROM table_name
