24.6. More Database Practice¶
In the previous pages, we created a database, added a table to it, and saved several entries in that table. Now we will learn how to modify the stored data.
24.6.1. Update Table Data¶
By using an UPDATE query, we can change one or more entries in a table. Code along with the following video to practice this technique.
Note
The video shows a new column in the students table. Here’s how to add
that column and fill it with 'Yes' strings:
6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | # Add the recent_grad column to the students table.
sql_query = "ALTER TABLE students ADD COLUMN recent_grad TEXT"
cursor.execute(sql_query)
# Fill each cell in the column with a 'Yes' string.
sql_query = "UPDATE students SET recent_grad = 'Yes'"
cursor.execute(sql_query)
database.commit()
|
After running this code, your students table should match the one shown
at the beginning of the video.
Key points:
The
UPDATEquery uses theSETkeyword to identify one or more columns to change.To identify which rows to change, the
UPDATEquery should also include aWHEREcondition. If we leave out the condition, then every row in the table will be modified.Combining
SETandWHEREidentifies which cell(s) in the table to change.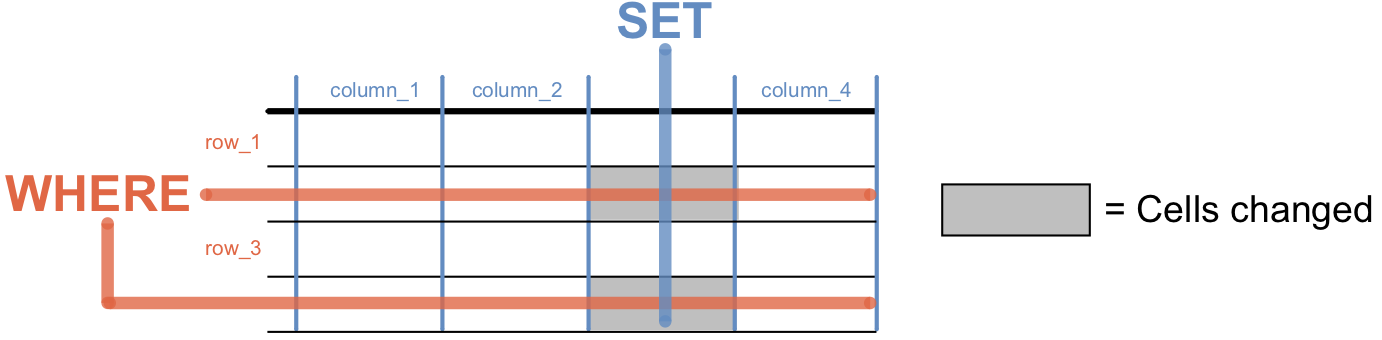
Each cell in the table has a (column, row) position.¶
After running the query, use the
.commit()method to confirm the changes.After we commit an
UPDATEquery, there is no quick Undo option!
Sample code:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | import sqlite3
database = sqlite3.connect('practice.db')
cursor = database.cursor()
# Update selected cells from the 'students' table:
sql_query = "UPDATE students SET recent_grad = 'No' WHERE grad_year < 2017"
cursor.execute(sql_query)
database.commit()
|
24.6.2. Delete Data¶
Code along with the following video to practice removing rows from a table. Also learn how to delete an entire table from the database.
Key points:
The DELETE FROM query removes selected rows from a table.
Add a
WHEREclause to identify which rows should be deleted.The
DROP TABLEquery removes an entire table from the database. ALL the row and column information will be deleted.There is NO undo option for a
DELETEorDROPquery.
Sample code:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | import sqlite3
database = sqlite3.connect('practice.db')
cursor = database.cursor()
# Delete selected rows from the 'students' table:
sql_query = "DELETE FROM students WHERE recent_grad == 'No'"
cursor.execute(sql_query)
database.commit()
# Drop the 'remove_me' table from the database:
sql_query = "DROP TABLE remove_me"
cursor.execute(sql_query)
|
24.6.3. Check Your Understanding¶
Question
Assume we have a table called books stored in our database. The table
includes columns for title, publish_date, and category.
Which SQL query returns the titles for all non-fiction books published
after 2019?
- SELECT title, category FROM books WHERE publish_date > 2019
- SELECT publish_date > 2019 FROM books WHERE category = 'non-fiction'
- SELECT books, title WHERE publish_date > 2019 AND category = 'non-fiction'
- SELECT title FROM books WHERE publish_date > 2019 AND category = 'non-fiction'
Question
What should you do if you accidentally DROP a table from your database
or DELETE the wrong row from a table?
- Accept that the data is gone and learn from your mistake.
- Cry.
- Blame someone else.
- Use Control-z to undo the mistake.
Question
To UPDATE an entry in a table, the SQL query should specify a row and a
column. Which keyword identifies the rows to change, and which keyword
identifies the columns?
- SET identifies the rows. WHERE identifies the columns.
- SET identifies the columns. WHERE identifies the rows.
- FROM identifies the rows. SET identifies the columns.
- FROM identifies the columns. WHERE identifies the rows.
