9.1. Design Patterns, MVC, and Spring, Oh My!¶
So far, we have been designing our applications by diagramming classes, drawing connections, and abstracting via interfaces.
This practice benefits us because we can start seeing issues before we start coding.
Many software developers start their applications with this process.
Before we start diagramming our Cat class and our HouseCat class, we decide on the template for our design that we want to use.
These design templates that are abstract solutions to common software architecture problems are called design patterns.
Design patterns provide a set of conventions that we follow to build an application.
Model-View-Controller (MVC) is a design pattern where the programming logic behind the application is broken down into 3 components: models, views, and controllers. A model handles the data and business logic of the application. A view handles the user interface elements. A controller passes information from the models to the views. Controllers are the traffic cops of the application, capable of passing data back and forth to the browser in MVC web applications. This process will be covered in depth later on in this chapter.
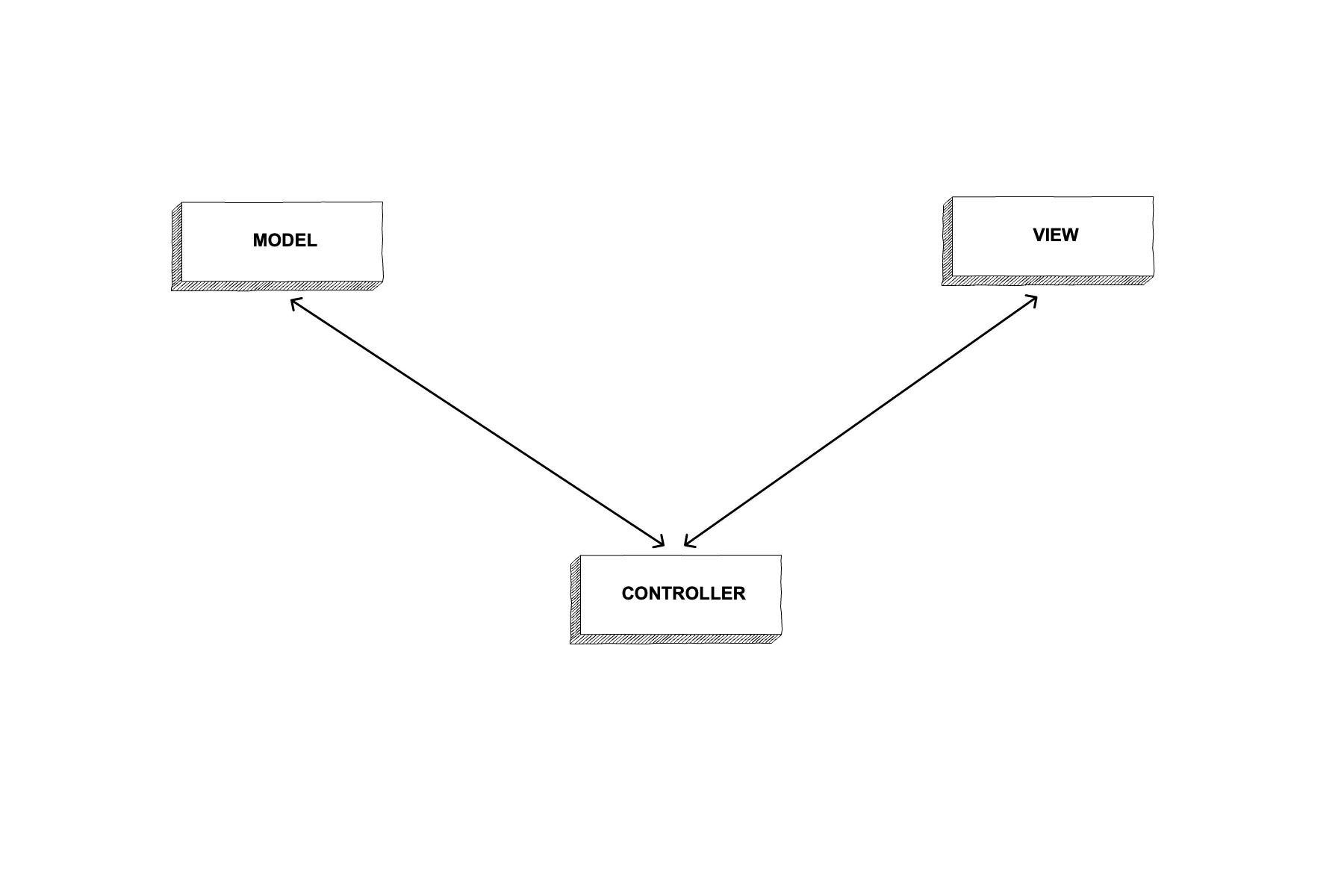
Because MVC breaks down all of the programming logic of an application into three digestable components, we can use this particular design pattern to make extensible applications. We also use MVC because it separates the components of the programs that the user interacts with from the underlying business logic.
9.1.1. Spring¶
Spring is a Java framework with multiple different modules and extensions. For this class, we will be using Spring Boot, an extension of Spring MVC (a module of Spring) to build Java based web applications with the MVC design pattern. Spring Boot gives us easier configuration options than Spring MVC and is a framework that helps us write applications with the idea of convention over configuration. With Spring Boot’s default settings and locations, we won’t have to configure all of the paths and settings for our applications. We can also write and run apps quickly because of the embedded application server, Tomcat.
9.1.2. How we Teach Spring¶
The following section is the first of many videos we will be using to demonstrate coding a Spring Boot application. The video below introduces the role of controllers. In subsequent videos, we ask you to code along for maximum absorption of the topics introduced. A summary of the content introduced will follow each video.
