8.4. Multi-Dimensional Arrays¶
Earlier we learned that arrays can store any type of value. If that is true, can we store arrays inside of arrays? Well yes we can....
A multi-dimensional array is an array of arrays, meaning that the values inside the array are also arrays. The inner arrays can store other values such as strings, numbers, or even more arrays.
The figure below demonstrates a synonyms array that has arrays as values. The inner arrays contain words that are synonyms of each other. Notice each inner array has an index position.
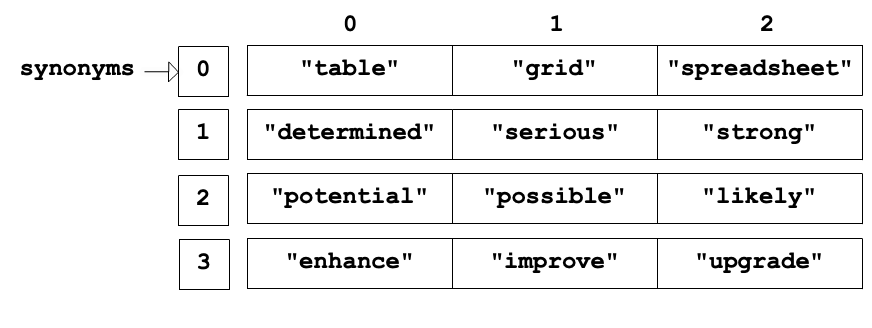
8.4.1. Two Dimensional Arrays¶
The simplest form of a multi-dimensional array is a two dimensional array. A two dimensional array is like a
spreadsheet with rows and columns. To access items in a two dimensional array, use square bracket notation and
two indexes array[0][0]. The first index is for the outer array, or the "row", and second index is for the inner array,
or the "column".
Note
The row and column analogy is used to help visualize a two dimensional array, however it's not a perfect analogy. There are no specific JavaScript language rules forcing the inner arrays to all have the same length. The inner arrays are separate arrays that can be of different length.
Example
Use a two dimensional array to contain three different lists of space shuttle crews.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | let shuttleCrews = [
['Robert Gibson', 'Mark Lee', 'Mae Jemison'],
['Kent Rominger', 'Ellen Ochoa', 'Bernard Harris'],
['Eilen Collins', 'Winston Scott', 'Catherin Coleman']
];
console.log(shuttleCrews[0][2]);
console.log(shuttleCrews[1][1]);
console.log(shuttleCrews[2][1]);
|
Console Output
Mae Jemison
Ellen Ochoa
Winston Scott
8.4.2. Multi-Dimensions and Array Methods¶
In a multi-dimensional array, both the inner and outer arrays can be altered with array methods. However, bracket notation must be used correctly.
To apply a method to the outer array, the syntax is:
multiArrayName.method();
To apply a method to one of the inner arrays, the syntax is:
multiArrayName[indexOfInnerArray].method();
Example
Use array methods to add an additional crew array and alter existing arrays.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | let shuttleCrews = [
['Robert Gibson', 'Mark Lee', 'Mae Jemison'],
['Kent Rominger', 'Ellen Ochoa', 'Bernard Harris'],
['Eilen Collins', 'Winston Scott', 'Catherin Coleman']
];
let newCrew = ['Mark Polansky', 'Robert Curbeam', 'Joan Higginbotham'];
// Add a new crew array to the end of shuttleCrews
shuttleCrews.push(newCrew);
console.log(shuttleCrews[3][2]);
// Reverse the order of the crew at index 1
shuttleCrews[1].reverse();
console.log(shuttleCrews[1]);
|
Console Output
Joan Higginbotham
[ 'Bernard Harris', 'Ellen Ochoa', 'Kent Rominger' ]
8.4.3. Beyond Two Dimensional Arrays¶
Generally, there is no limit to how many dimensions you can have when creating arrays. However it is rare that you will use more than two dimensions. Later on in the class we will learn about more collection types that can handle complex problems beyond the scope of two dimensional arrays.
8.4.4. Check Your Understanding¶
Question
What are the two dimensional indexes for "Jones"?
1 2 3 4 | let school = [
["science", "computer", "art"],
["Jones", "Willoughby", "Rhodes"]
];
|
How would you add "dance" to the array at school[0]?
How would you add "Holmes" to the array at school[1]?
