grep From STDIN
grep from STDIN
So far you have only used grep to search a specific file. However, you can pass input directly to grep and match STDIN results against a Regular Expression pattern.
ls | grep Example
Match patterns for all contents of the home directory:
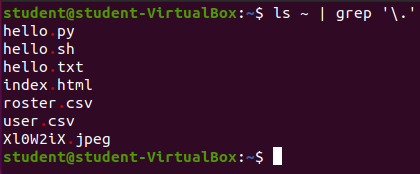
Match all files with a . in our home directory.
ls ~ | grep '\.'Output:
Note
The . is a Regular Expression special symbol meaning to match any character. In order to search for an actual . you need to escape the . so that RegEx knows that you are searching for an actual period and not referencing special symbol. The escape special symbol in RegEx is the backslash \ symbol.
When you provide the regular expression: '\.' you are telling grep to match any lines that have a . in them.
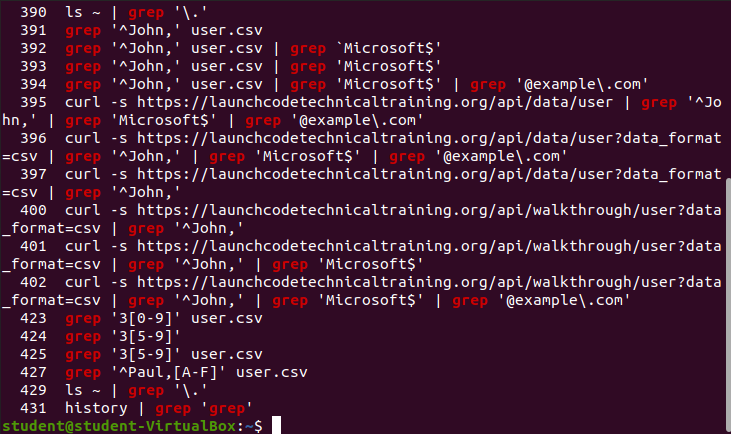
history | grep Example
Match all grep commands in our bash history
history | grep 'grep'Output:
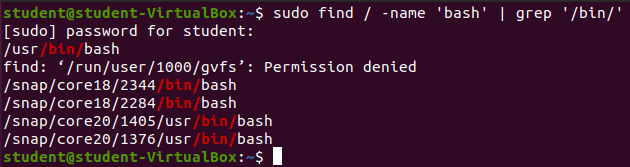
find | grep Example
Match all /bin/ for files containing the word bash in the root directory.
sudo find / -name 'bash' | grep '/bin/'Output:
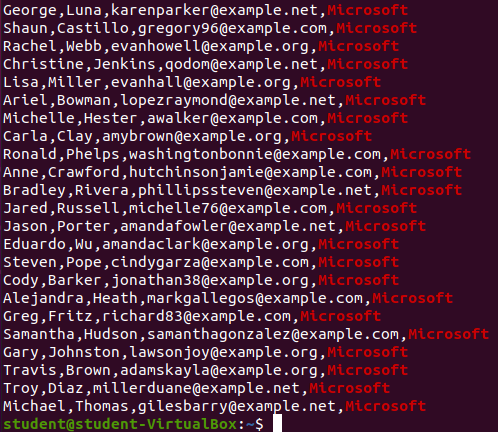
curl | grep Example
Send a curl request directly to the API and match the results (csv in STDIN) to a specific pattern.
curl -s https://launchcodelearning.org/api/walkthrough/user?data_format=csv | grep 'Microsoft$'Output: