Changing File Ownership
Name
chown- change file owner and group
Usage
The chown command allows you to change the ownership on any given file which will directly affect what users are able to read, write, and execute the target file.
chown [OPTION] [OWNER][:[GROUP]] [file-name]Examples
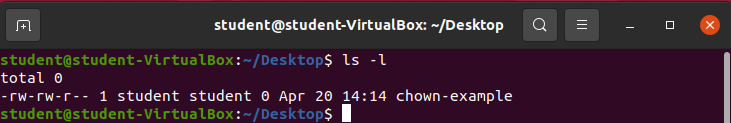
Create a new file called chown-example.
touch chown-exampleCheck the current owner of the newly created file:
ls -lOutput:
The current user student in the student group is the owner of the file chown-example.
Change File Owner
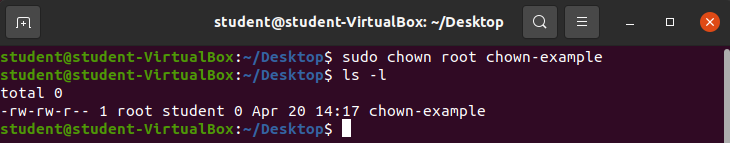
Change the ownership of the file chown-example to the root user.
sudo chown root chown-exampleOutput:
The new owner of the file chown-example has been changed to the root user. However the chown-example file still falls within the student group.
Change File Group
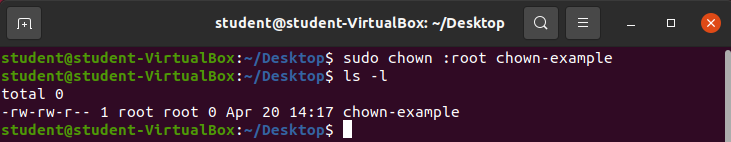
To change the group of a file chown requires an additional argument:
sudo chown :root chown-exampleOutput:
You are able to add a : to the chown argument to change the group of a file.
Bonus
Recap:
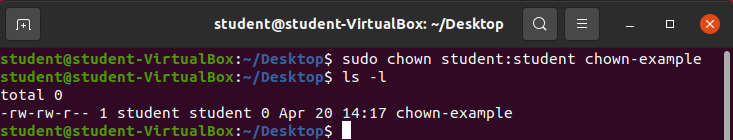
chowncommand- allows you to change user and group ownership of a file
chown [OPTIONS] file-namechown new-user file-name: changes user ownershipchown :new-group file-name: changes group ownershipchown new-user:new-group file-name: changes both user and group ownership with one command