Variables
Creating Bash Variables
Bash is able to hold values within a named variable similar to programming languages like Java, JavaScript, Python, and many more.
Notice how bash uses the equal sign (=) as an assignment operator.
name="John"name = "Paul"let name = "Paul";String name = "John";Note
Similar to Python, Bash will respect any type of value you assign to a variable.
Syntax for initializing a variable in bash:
variable=value_to_holdTwo notes about bash variables:
- Bash variables do not support whitespace on either side of the equals or
=sign. - To reference a bash variable you need to use a
$in front of the variable name.
Creating a Variable
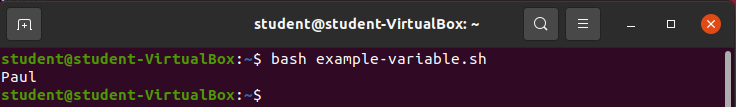
Create a new file called example-variable.sh
name="Paul"
echo $nameAdd the above code to the file.
Run the command bash example-variable.sh
More Examples
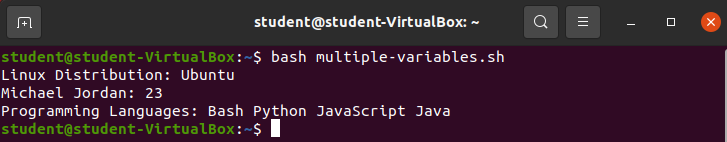
Create a file called multiple-variables.sh
#!/bin/bash
## Variable holding the string "Ubuntu"
linux_distro="Ubuntu"
##Variable holding the number 23
number=23
##Arraylist holding multiple strings
language_list=("Bash" "Python" "JavaScript" "Java")
echo "Linux Distribution: " $linux_distro
echo "Michael Jordan: " $number
echo "Programming Langauges :" "${language_list[@]}"Add the above code to the file.
Run the command bash multiple-variables.sh
Recap:
How to create variables in Bash:
variable=value_to_hold- Bash variables are not type specfic
- Reference a bash variable with the
$