Demo
Demo: Creating & Executing a Bash Script
Warning
This file is written as instructions for an instructor-led demo. As a student you probably can work through this file on your own, but it does a few things that we haven’t learned or practiced yet. You very possibly could get stuck and will not receive guidance on moving through any issues you encounter. That being said, you can attempt this demo and work through the issues you encounter as practice for attempting to learn on your own and troubleshooting issues as they arise.
In this Demo your instructor will show you how to create and execute a bash script, how to add to the $PATH Shell Variable, and how to create a SymLink. This demo will also give a sneak peek into creating directories and files from the Bash shell.
Create Directory & File
mkdir /home/student/bintouch /home/student/bin/whattimeisit
Add the following text into the file. You may find nano to be useful, but feel free to edit the file however you want.
#!/bin/bash
echo "Hello Paul..."
echo "It is currently $(date)"
echo "Have a nice day!"Execute the file using the Bash command
- run the file:
bash /home/student/bin/whattimeisit
Make the file executable & execute in new ways
- make the file executable:
chmod +x /home/student/bin/whattimeisit - run the file:
/home/student/bin/whattimeisit- or:
./bin/whattimeisit - or:
bash /home/student/bin/whattimeisit
- or:
Adding /home/student/bin to $PATH
- what is the shells $PATH:
echo $PATH - update the PATH variable with our personal bin:
PATH=$PATH:/home/student/bin - check $PATH for the new information:
echo $PATH
Execute the program directly from $PATH
whattimeisit
Rename file
- what if I want to change the name of my program?
mv /home/student/bin/whattimeisit /home/student/bin/when
Run same program with new name
when- can you run the old name?
whattimeisit - can you run it directly with bash?
bash /home/student/bin/when- can you run it the other ways we tried above?
How can we view the absolute path of the when program?
- what happens if we:
which when
Does the when program have a man page?
- what happens if we:
man when
Symlink
Where is python?
- python comes standard as a part of most Linux distros
which python–> so where is it?which python3–> here it is (python 2 is dead and has been fully replaced by python3) –> older versions of Ubuntu did have python which defaulted to Python2 & also had a version of Python3 installed.
Manually search for python3 in /usr/bin
ls /usr/bin- python should be here, manually search for it
- why is
python3blue? - why is there a
python3.8that is green?- when we made our Bash script executable it turned green
- are all executables green?
- why is
- python should be here, manually search for it
Take a deeper look at the file metadata
could do it manually with
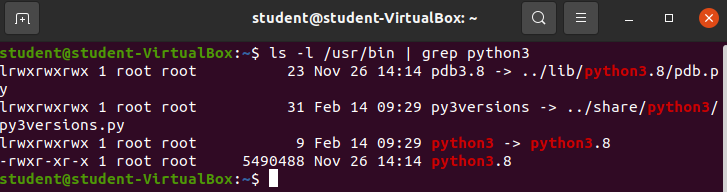
ls -l /usr/bin, but that would take a whilelet’s use grep to search for the output we want instead:
ls -l /usr/bin | grep python3
What is python3 -> python3.8 representing? It looks like python3 is a shortcut to python3.8!
- what is a Symlink?
- it really is just a shortcut
- soft link
- both
python3andpython3.8should execute the same program- Enter
python3 --version&python3.8 --version- same program!
- Enter
Edit our Bash script to be executable with a SymLink
Change name back to whattimeisit
mv /home/student/bin/when /home/student/bin/whattimeisit
Create a SymLink pointing to whattimeisit named when
ln -s /home/student/bin/whattimeisit /home/student/bin/when- look at the contents of the
/home/student/bindirectory:ls -l /home/student/bin
How can we run the program?
whattimeisitwhen
This explains what Python3 is in /usr/bin – just a symlink pointing at the actual python3.8 interpreter!
Note
In Ubuntu the color scheme of STDOUT is helpful. Green files are executable, light blue files are SymLinks, dark blue files are directories, white files are standard files. Not all terminal emulators support color, but it is quite useful when it is around.