17.3. Visual Studio Code¶
Before we dive into coding our first local program, let’s take a moment to get used to our new code editor.
Open the Visual Studio Code program and take a look around.
17.3.1. Welcome Screen¶
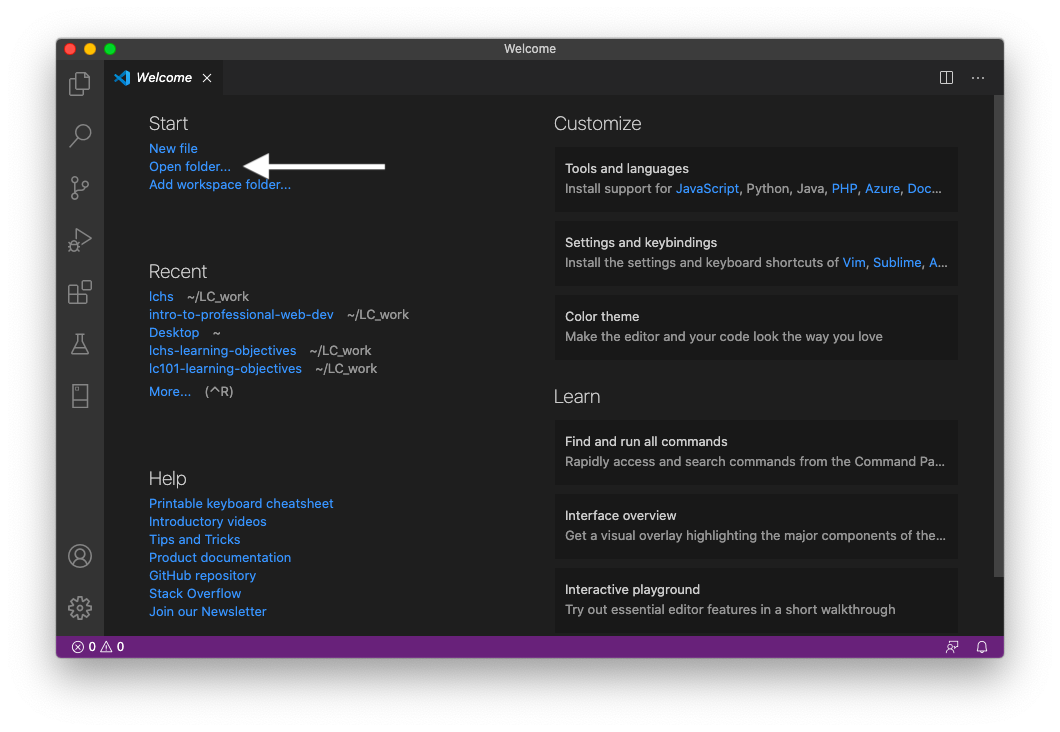
The first time we run VS Code, the program displays the Welcome screen to get us started. Go ahead and click the Open Folder option and then select the Desktop directory. (Opening any directory activates the workspace, but for now we will practice on the Desktop).
Note
When we launch VS Code, it tries to open the last project we worked on. If this happens now, don’t worry. Select New Window from the File menu to bring up the Welcome screen.
Welcome to Visual Studio Code!¶
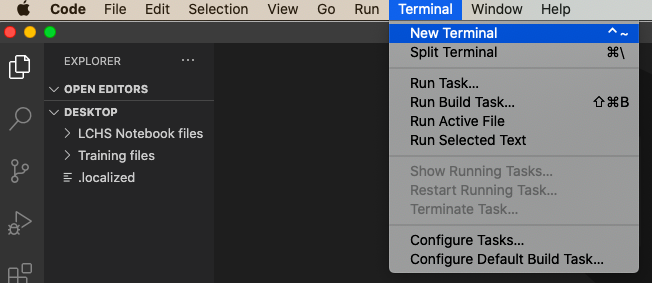
Next, click on the Terminal menu and select New Terminal.
Open the terminal inside VS Code.¶
We now have several different panels, buttons, and menus that allow us to edit, debug, and run our code.
17.3.2. The Workspace¶
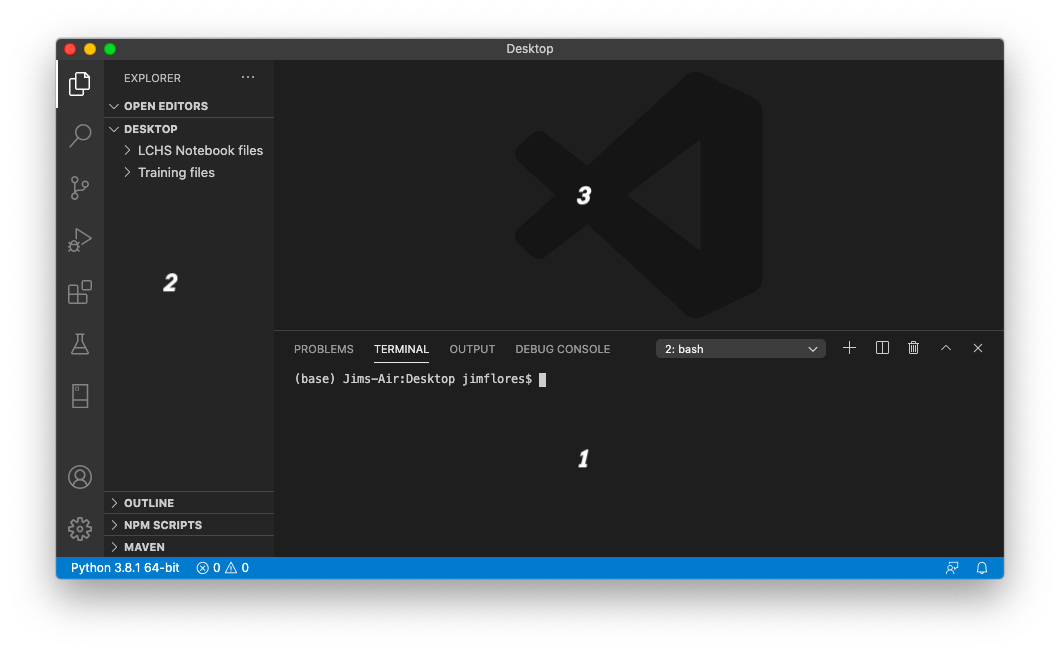
The workspace in Visual Studio Code consists of three main panels:
The VS Code workspace.¶
Terminal Panel: VS Code allows us to run our terminal application inside the workspace. All of the actions we practiced in the Terminal chapter will work here.
Activity Bar and File Tree: This panel lets us navigate the file system, perform searches, install extensions, update the software, etc.
Editor Panel: Our code goes here! VS Code recognizes most major programming languages.
17.3.3. Terminal Panel¶
Let’s run a couple of terminal commands just to see where we are:
1 2 3 4 | Jims-Air:Desktop jimflores$ pwd
/Users/jimflores/Desktop
Jims-Air:Desktop jimflores$ ls
LCHS Notebook files Training files
|
Take a look at the file path returned by pwd. By opening the Desktop folder
from the Welcome screen, VS Code automatically put us in that directory when we
opened the terminal.
The ls command displays the files and folders currently in Desktop.
Notice how the same items appear in the file tree on the left side of the
workspace.
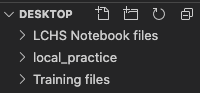
Now use the terminal to create a new directory in the Desktop:
1 2 3 | Jims-Air:Desktop jimflores$ mkdir local_practice
Jims-Air:Desktop jimflores$ ls
LCHS Notebook files Training files local_practice
|
Check your computer to see that a local_practice folder appeared on the
Desktop.
When we write our first local Python program, we will use the terminal to run that code.
17.3.4. Activity Bar and File Tree¶
The Activity Bar on the left side of the workspace contains several buttons, but we will only look at three of them right now.
File Explorer: Clicking on the top icon hides/reveals the file tree for the current directory.
Clicking on the
>symbol next to a folder displays the contents of that directory.Clicking on a file name opens that file in the editor.
The file tree includes buttons for adding new files and folders to the current directory.
Settings: Clicking on the gear icon at the bottom of the toolbar brings up options for customizing the workspace. For example, if you don’t like the default theme (dark background with light text), you can change it!
Extensions: We can install, update, or uninstall extensions for VS Code. Click on the fifth icon from the top to make sure that extensions for Python and HTML/CSS are installed. If not, follow the instructions in the Setting Up VS Code appendix to add them.
17.3.4.1. Add a New File¶
Click on the File Explorer icon to display the file tree.
Select the
local_practicedirectory, which is currently empty.Click on the New File button.
Notice that a space opens under the
local_practicedirectory where we can enter a filename. Typehello.pyand hit Enter.A
hello.pytab appears in the editor panel. We will add some code to this file soon.
Note
The .py extension indicates that the file contains Python code. Remember
to add this extension to all of your Python programs!
17.3.5. Editor Panel¶
This is where we will do most of our work in VS Code. From our practice in repl.it and Trinket, we are familiar with the features of a code editor.
Fun Fact
The developers behind repl.it modeled their editor on the look of Visual Studio Code!
Now let’s do some local coding!
17.3.6. Check Your Understanding¶
Question
In VS Code, how do we add a new file to a directory? Select ALL correct options.
- Click on the directory in the file tree and press the New File button.
- Click on the directory in the file tree and press the New Folder button.
- In the terminal, navigate to the directory and use touch new_filename.
- In the terminal, navigate to the directory and use mkdir new_filename.
