You already know one method for creating a function:
1function myFunction(parameter1, parameter2,..., parameterN) {
2
3 // function body
4
5}
A function defined in this way is a named function (myFunction, in the example above).
Many programming languages, including JavaScript, allow us to create anonymous functions, which do not have names. We can create an anonymous function by simply leaving off the function name when defining it:
1function (parameter1, parameter2,..., parameterN) {
2
3 // function body
4
5}
You might be asking yourself, How do I call a function if it doesn't have a name?! Good question. Let's address that now.
Anonymous functions are often assigned to variables when they are created, which allows them to be called using the variable's name.
Example
Let's create and use a simple anonymous function that returns the sum of two numbers.
1let add = function(a, b) {
2 return a + b;
3};
4
5console.log(add(1, 1));
Console Output
2
The variable add refers to the anonymous function created on lines 1 through 3. We call the function using the variable name, since the function doesn't have a name.
The visual analogy here is the same as that of a variable referring to a named function.
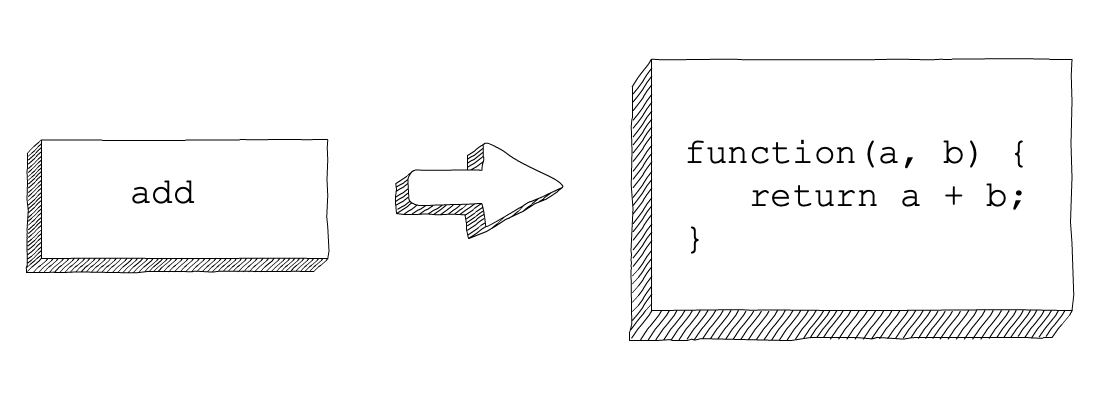
A variable that refers to an anonymous function.¶
Warning
Like other variable declarations, an assignment statement using an anonymous function should be terminated by a semi-colon, ;. This is easy to overlook, since named functions do not end with a semi-colon.
Question
Convert the following named function to an anonymous function that is stored in a variable.
1function reverse(str) {
2 let lettersArray = str.split('');
3 let reversedLettersArray = lettersArray.reverse();
4 return reversedLettersArray.join('');
5}
Question
Consider the code sample below, which declares an anonymous function beginning on line 1.
1let f1 = function(str) {
2 return str + str;
3};
4
5let f2 = f1;
Which of the following are valid ways of invoking the anonymous
function with the argument "abcd"? (Choose all that apply.)
f1("abcd");function("abcd");f2("abcd");Question
Complete the following code snippet so that it logs an error message
if userInput is negative.
1let logger = function(errorMsg) {
2 console.log("ERROR: " + errorMsg);
3};
4
5if (userInput < 0) {
6 ____________("Invalid input");
7}