Instead of using GET and query parameters to submit form data, we can use POST.
To submit a form using a POST request, set the form's method attribute to "POST".
Form data submitted via POST will be submitted in the body of the HTTP request.
Data submitted by GET requests is less secure than POST because GET request URLs
and the query parameters are cached and logged, possibly leaking sensitive data.
Example
Form with method="POST"
<form action="" method="POST">
<label>Username <input type="text" name="username"></label>
<label>Team Name <input type="text" name="team"></label>
<button>Submit</button>
</form>
The action and method attributes allows us to choose where the form request will be
sent and what type of request will be sent. How do we configure what happens in response to
a form submission?
Form handlers are web server actions that receive, inspect, and process requests. They then send a response to the client. For this unit we are going to use form handlers that have already been created for us.
Example
When submitted, this form will send a POST request to the form handler defined by the
action attribute.
1<form action="https://handlers.education.launchcode.org/request-parrot" method="POST">
2 <label>Username <input type="text" name="username"></label>
3 <label>Team Name <input type="text" name="team"></label>
4 <button>Submit</button>
5</form>
Try It!
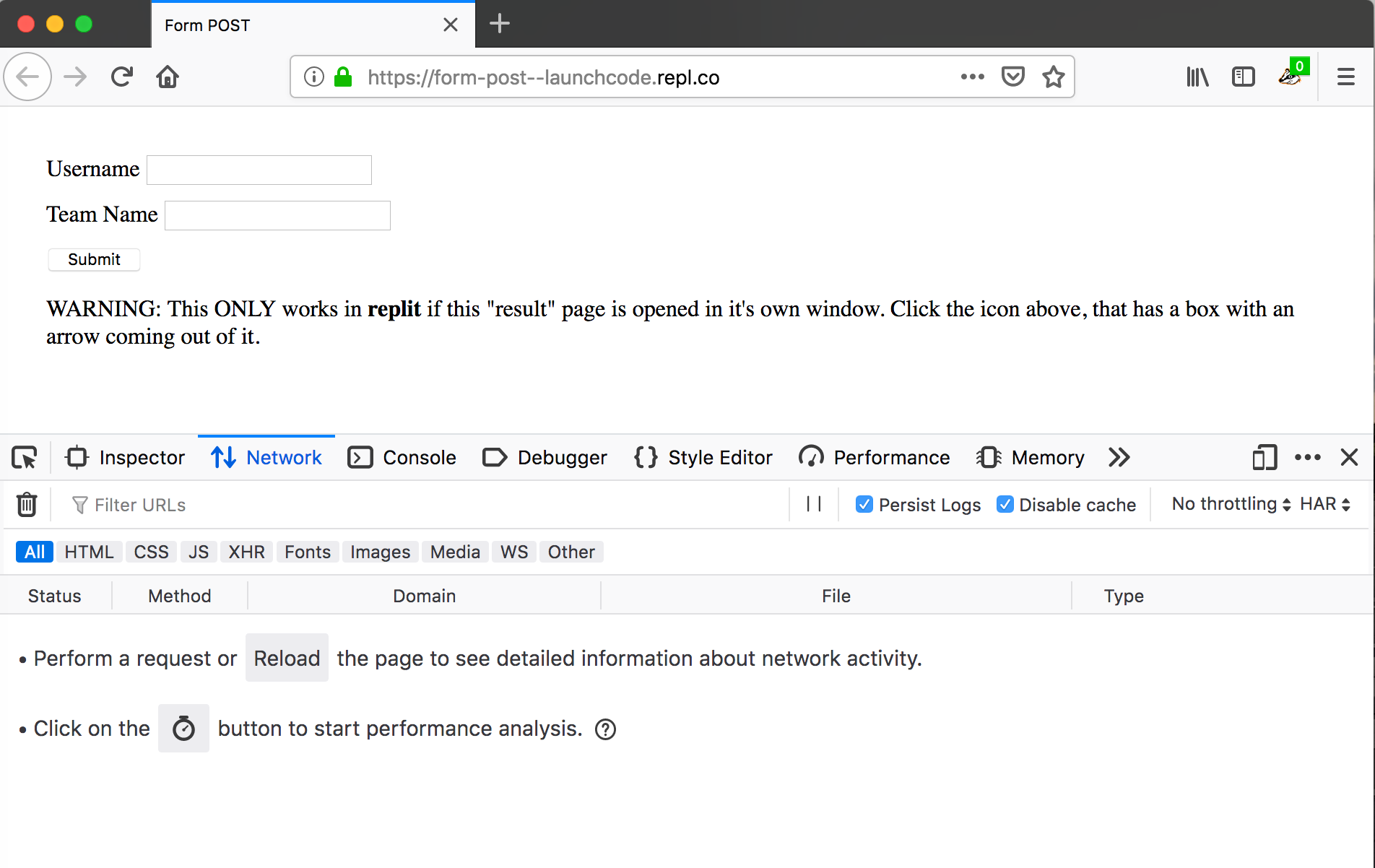
Firefox browser with form loaded, network tab open, and Persist logs checked¶
tracking into Username inputRequests into Team Name input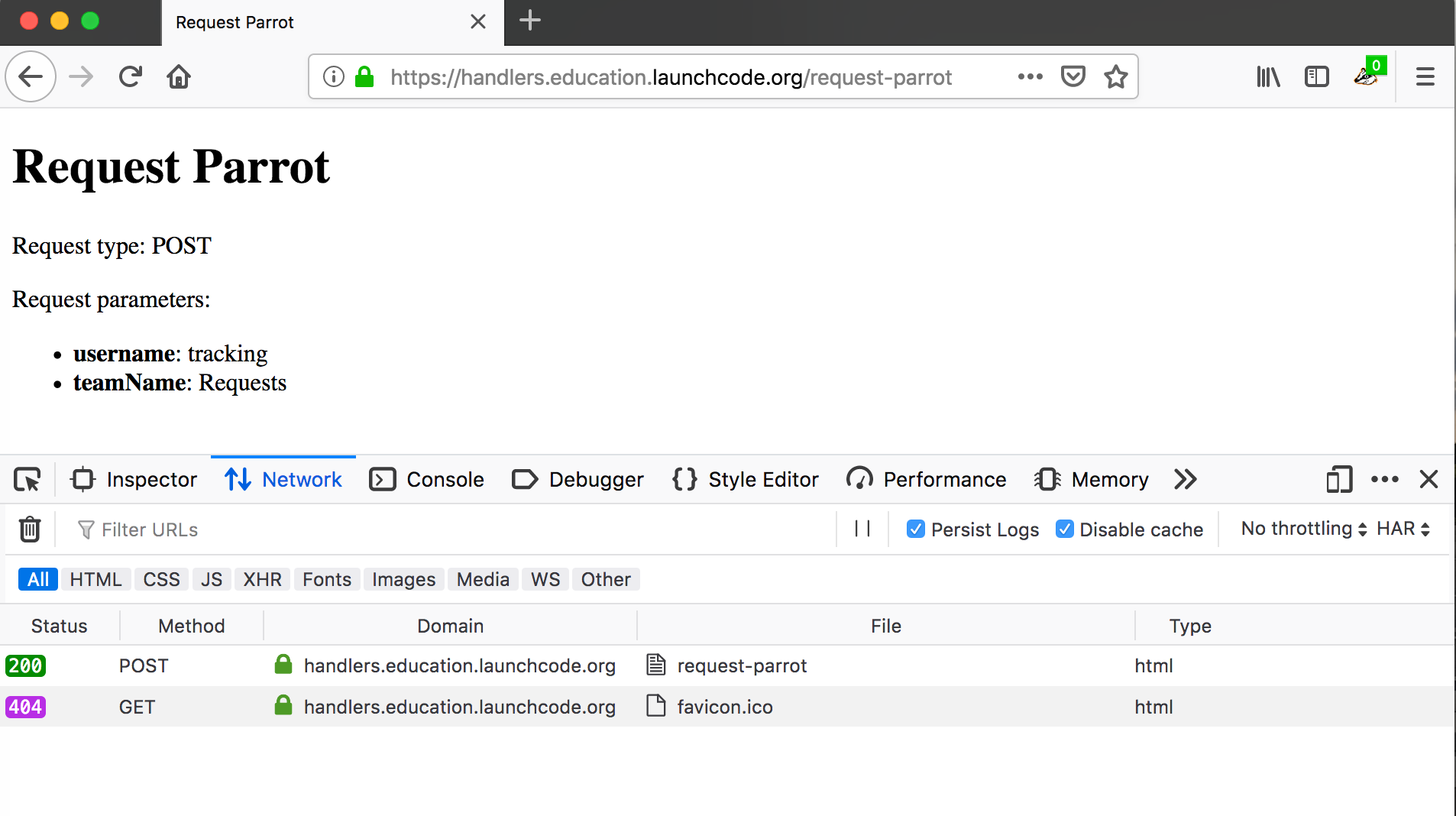
Firefox browser with request handler loaded and network tab showing requests¶
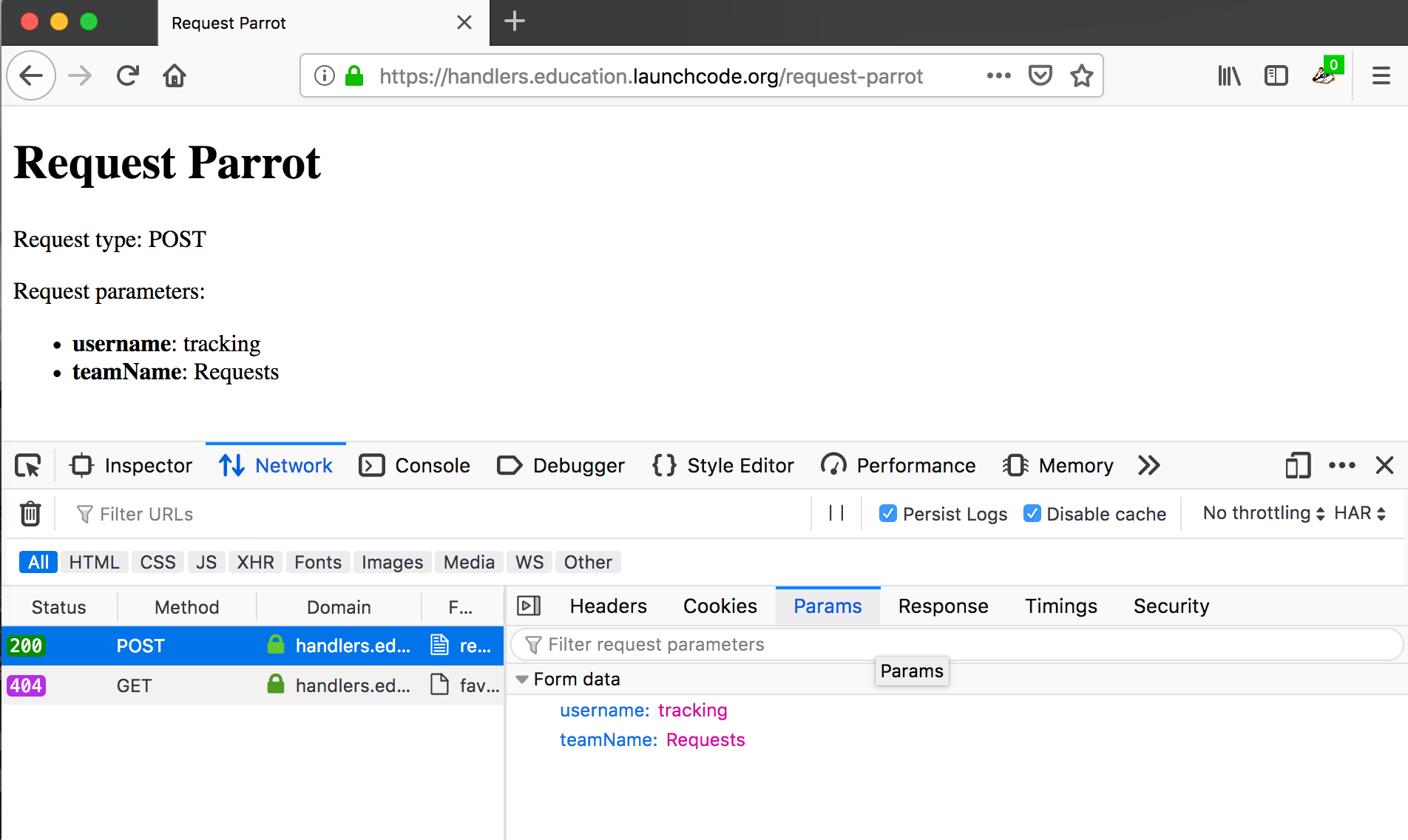
POST request highlighted with Params tab open showing Form data¶
Warning
Using POST for form submissions adds a very low level of security. Using HTTPS instead of HTTP adds a higher level of security. Configuring HTTPS is beyond the scope of this class.
Question
What attribute on <form> determines if the form is submitted with GET or POST?
Question
What attribute on <form> determines where the request is sent?