Models in MVC
In the previous chapters, you learned about thymeleaf, which displays data and an
interface for a user, and controllers which determine what data to send to the views.
This data needs to come from some source and take some shape. Cue the models.
What is a Model?
A model represents the logic for accessing and storing the data used in an application. Properly constructed, they do not depend on any controllers or views, which makes models easy to reuse without modification.
Models are not the data itself, but rather the data logic. They dictate how we want to handle the data in an application-specific way. The data used in an application is often sourced from a database or an external data service. Data is typically application-agnostic and it is the work of the models we write to shape raw data into useful application information.
Consider a physical address book (a model). It stores names, addresses, phone numbers, etc. on its pages. Anyone (a controller) can pick up the book, retrieve the information, and then write some of the data on a separate piece of paper (a view). The address book model does not depend on who picks it up and enters their contacts. The book just provides organization and storage logic. On the flip side, the same person can input the same contact data into a different book. So a model takes raw information and turns it into something useful for a particular application.
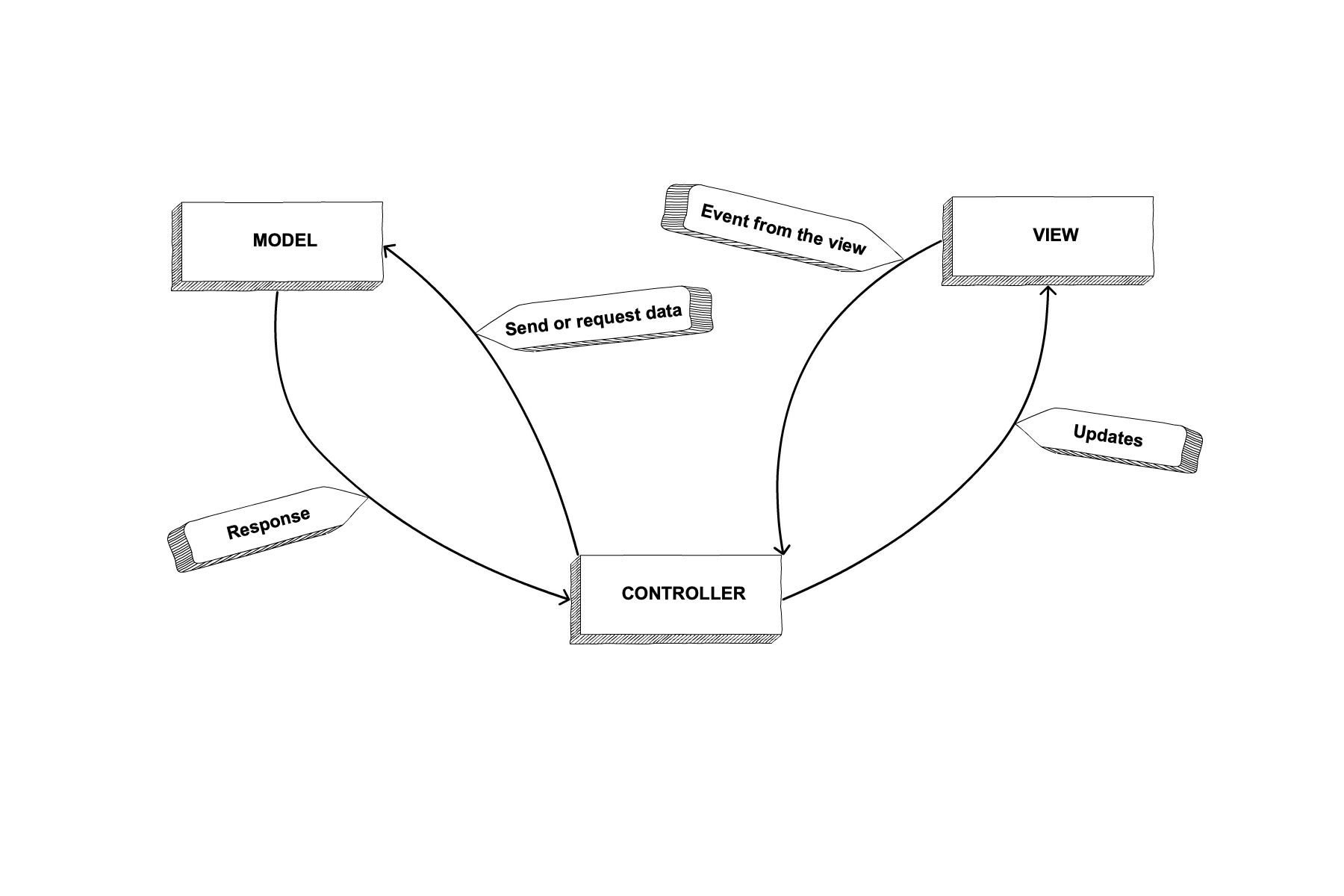
MVC: Putting it Together
Model
Shapes data to fit the needs of an application.
View
Displays data to the user. Via events, the user interacts with the view and updates the program data. The view communicates with the controller but not the model.
Controller
Directs the flow of information between the view and the model. It does not store the data or determine how to display it for the user. It passes information retrieved from the view to update the model. And it passes information retrieved from the model to update the view.
Need further review? Check out MVC for Noobs .
Model vs. Controller
One tricky part of using the MVC structure is deciding what code belongs in the model and what belongs in the controller. In general, any code that deals with data transfer or responding to user actions belongs in the controller. Code that involves retrieving data from a database or service or organizing that data belongs with the model.
In our codingevents application thus far, we’ve done all data handling inside of
controller classes. However, most data manipulation should occur in model classes.
So we need to make a distinction between these actions. For any manipulations that must occur
regardless of a user’s actions, that code belongs in the model. For changes
that vary depending on a user’s request (e.g. multiplying vs. adding a set of
numbers), that code belongs in the controller.
Model code defines the logic for processes that the user never needs to see. These include:
- The mechanics for storing data.
- The mechanics for retrieving data.
- The mechanics for organizing data.
- Updating or manipulating the data independent of any controller or view actions.
Controller code handles requests made by the user. These include:
- “Please retrieve this information from the model.”
- “Please store this according to the rules of the model.”
- “Please delete this item.”
- “Please change this item.”
- “Please display this.”
- “Please modify this data in a novel way”.
Remember, the controllers are the traffic cops, directing information from one place to another. A controller does not permanently store data. Instead, it either sends the information to the model, which uses its own code to preserve the data, or it sends the content to the view for display.
Check Your Understanding
If we use baking as an analogy for an MVC project, which of the following items best represents a model?
- The bread ingredients: flour, water, yeast, salt
- Mixing and shaping the ingredients together
- Baking the loaves into the final product
- Eating the bread
If we use a library as an analogy for an MVC project, which of the following items best represents a model?
- The books on the shelves
- The Dewey Decimal storage system
- The librarians
- The book readers