Task 4: Use Unit Testing to Verify Parts of the Job Class
Instead of manually creating sample Job objects to verify that your class works correctly, you will use unit tests instead.
Navigate to the package org.launchcode.techjobs.oo.test package and open the JobTest class. This file will hold all of the tests for the Job class.
Creating a JUnit Run Configuration
Since this project contains two sets of tests used for different purposes—the autograding tests and the JUnit tests you are about to write—we have to set up a run configuration to allow us to run them independently. We’ll show you how to do that now.
At the top right of IntelliJ, select Add Configuration, just left of the green Run button.
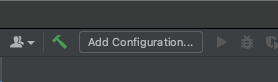
If this item doesn’t have the label Add Configuration, then open the associated dropdown and select Edit Configurations.
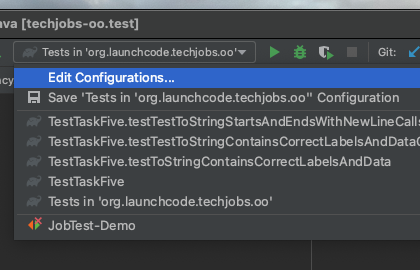
In the modal that opens, click on the + icon at the top left, and select JUnit.
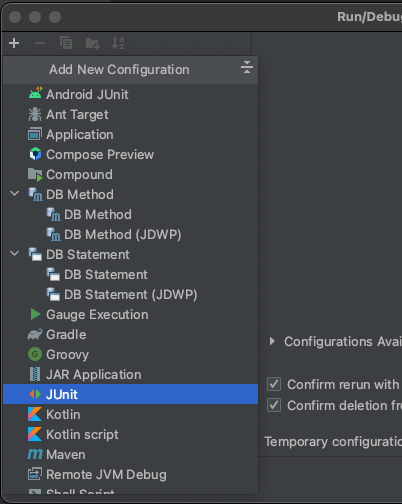
Fill out the resulting form using the values:
- Name: JobTest
- Java version: Java 17
- Module:
techjobs-oo-java17-graded.test - Class:
org.launchcode.techjobs.oo.JobTest(You will need to type or paste this. If the class contained a test, you could also click the icon at the right of this field and select the class from the window that opens.)
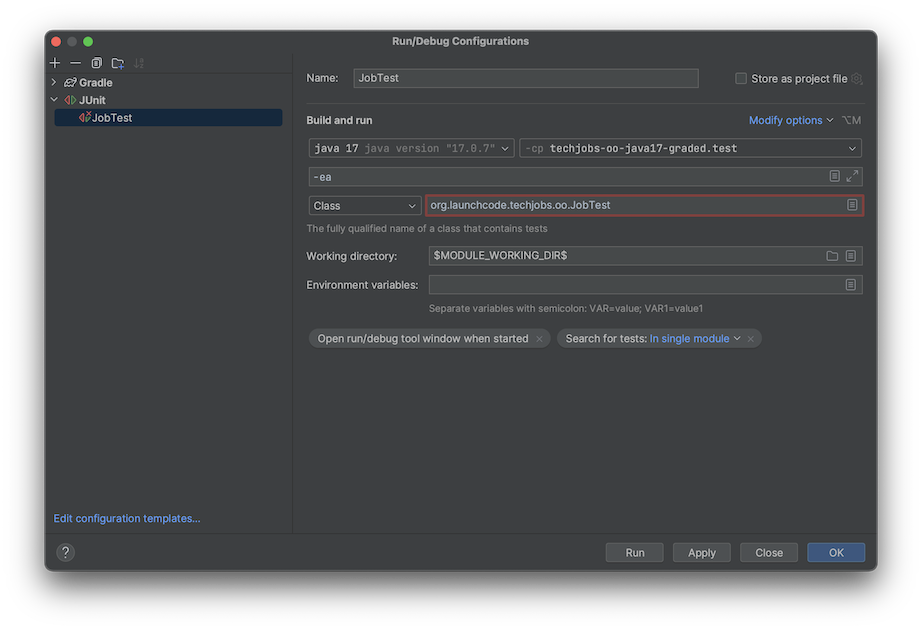
Ignore the message that says Class ‘org.launchcode.techjobs.oo.JobTest’ is not a test since you haven’t written any yet. Then hit Apply and OK.
To run the tests, select the JobTest configuration from the configurations menu and hit the green Run button.
Now you’re ready to start writing some tests!
Test the Empty Constructor
Each Job object should have a unique ID that is an integer.
In
JobTest, define a test calledtestSettingJobId. Do not forget to annotate it with@Test.Create two
Jobobjects using the empty constructor.Use
assertNotEqualsto verify that the IDs of the two objects are distinct.Run the test using the run configuration that you created above.
If the test doesn’t pass, what should be your first thought?
- “Drat! I need to fix the unit test.”
- “Drat! I need to fix my
Job()constructor code.”
WarningThe answer is NOT “1”.
Your test code might be incorrect, but that should not be your FIRST thought. TDD begins with writing tests for desired behaviors. If the tests fail, that indicates errors in the methods trying to produce the behavior rather than in the tests that define that behavior.
Test the Full Constructor
Each Job object should contain five fields (other than id) — name, employer, location, positionType, and coreCompetency. The data types for these five fields are String, Employer, Location, PositionType, and CoreCompetency, respectively.
In
JobTest, define a test calledtestJobConstructorSetsAllFields.Declare and initialize a new
Jobobject with the following data:new Job("Product tester", new Employer("ACME"), new Location("Desert"), new PositionType("Quality control"), new CoreCompetency("Persistence"));Use assertTrue and assertEquals statements to test that the constructor correctly assigns both the class and value of each field. Your test should have 5 assert statements of each type.
The instanceof keyword can be used to check the class of an object. The result of the comparison is a boolean.
The instanceof keyword can be used to check the class of an object. The result of the comparison is a boolean.Test the equals Method
Two Job objects are considered equal if they have the same id value, even if one or more of the other fields differ. Similarly, the two objects are NOT equal if their id values differ, even if all the other fields are identical.
In
JobTest, define a test calledtestJobsForEquality.Generate two
Jobobjects that have identical field values EXCEPT forid. Test thatequalsreturnsfalse.
It might seem logical to follow up the false case by testing to make sure that equals returns true when two objects have the same ID. However, the positive test is irrelevant in this case.
The way you built your Job class, each id field gets assigned a unique value, and the class does not contain a setId method. You also verified that each new object gets a different ID when you tested the constructors. Without modifying the constructors or adding a setter, there is no scenario in which two different jobs will have the same ID number. Thus, we can skip the test for this condition.
Time to save, commit, and push your work to GitHub again.