With a User class in place, we can now create controllers and views for creating a user and verifying their credentials.
AuthenticationController¶In the controllers package, create a new class named AuthenticationController. Since this controller will deal with User objects, it needs a UserRepository instance.
21 22 23 24 25 26 27 | @Controller
public class AuthenticationController {
@Autowired
UserRepository userRepository;
}
|
Before creating handler methods for rendering and processing our login and registration forms, we need some utility methods for working with sessions. Below the definition of userRepository, let’s add the following class members:
27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 | private static final String userSessionKey = "user";
public User getUserFromSession(HttpSession session) {
Integer userId = (Integer) session.getAttribute(userSessionKey);
if (userId == null) {
return null;
}
Optional<User> user = userRepository.findById(userId);
if (user.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
return user.get();
}
private static void setUserInSession(HttpSession session, User user) {
session.setAttribute(userSessionKey, user.getId());
}
|
This code allows us to store and retrieve the login status of a user in a session. More specifically, a logged-in user’s user ID will be stored in their session.
| session_id | 81LfWG9 |
|---|---|
| user | 42 |
The static field userSessionKey is the key used to store user IDs. setUserInSession uses an HttpSession object (part of the standard javax.servlet.http package) to store key/value pair. getUserFromSession looks for data with the key user in the user’s session. If it finds one, it attempts to retrieve the corresponding User object from the database. If no user ID is in the session, or if there is no user with the given ID, null is returned.
Note
The HttpSession class handles the details of session creation and lookup for us, including generating unique session IDs and session cookies.
These utility methods will allow our handlers to manage authentication.
Our login and registration forms will use DTOs to help with form rendering and processing. Furthermore, since these forms will be similar—both require a username and password—we’ll use inheritance in creating our DTOs.
The DTO for the login form needs only username and password fields.
10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 | public class LoginFormDTO {
@NotNull
@NotBlank
@Size(min = 3, max = 20, message = "Invalid username. Must be between 3 and 20 characters.")
private String username;
@NotNull
@NotBlank
@Size(min = 5, max = 30, message = "Invalid password. Must be between 5 and 30 characters.")
private String password;
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
}
|
LoginFormDTO should live in the models.dto package.
Tip
To better understand this approach, think of a DTO associated with a form as an object that represents each of the form fields. Using a DTO to represent the data associated with a form makes form rendering and processing much easier when the form does not line up with a specific model class.
Note
In the class above, we have a password field that will store a plain-text password. However, this does not contradict our early imperative about NOT storing passwords, since LoginFormDTO is not a persistent class.
Our registration form will ask for a username/password pair, and then ask the user to confirm the password by typing it in again. So the associated DTO can extend LoginFormDTO and add an additional field for password verification.
6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | public class RegisterFormDTO extends LoginFormDTO {
private String verifyPassword;
public String getVerifyPassword() {
return verifyPassword;
}
public void setVerifyPassword(String verifyPassword) {
this.verifyPassword = verifyPassword;
}
}
|
RegisterFormDTO should also live in the models.dto package.
We are now ready to build our form handlers. Before we can authenticate a user, we must have users in the application, so we’ll build the registration form first.
To render the form within AuthenticationController is simple:
48 49 50 51 52 53 | @GetMapping("/register")
public String displayRegistrationForm(Model model) {
model.addAttribute(new RegisterFormDTO());
model.addAttribute("title", "Register");
return "register";
}
|
Note
When passing an object into the view with model.addAttribute, specifying a label for the object is optional. If a label is not specified the class name is used, with the first letter converted to lowercase.
In the method above, model.addAttribute(new RegisterFormDTO()) will pass a RegisterFormDTO object in with the label registerFormDTO.
The registration form (in templates/register.html) uses the three DTO fields to render the form fields:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 | <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org/">
<head th:replace="fragments :: head"></head>
<body class="container">
<header th:replace="fragments :: header"></header>
<form method="post">
<div class="form-group">
<label>Username
<input class="form-control" th:field="${registerFormDTO.username}" />
</label>
<p class="error" th:errors="${registerFormDTO.username}"></p>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>Password
<input class="form-control" th:field="${registerFormDTO.password}" type="password" />
</label>
<p class="error" th:errors="${registerFormDTO.password}"></p>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>Verify Password
<input class="form-control" th:field="${registerFormDTO.verifyPassword}" type="password" />
</label>
</div>
<input type="submit" class="btn btn-primary" value="Register" />
</form>
</body>
</html>
|
The form processing handler is more complicated. Let’s look at it, and then break it down in detail.
55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 | @PostMapping("/register")
public String processRegistrationForm(@ModelAttribute @Valid RegisterFormDTO registerFormDTO,
Errors errors, HttpServletRequest request,
Model model) {
if (errors.hasErrors()) {
model.addAttribute("title", "Register");
return "register";
}
User existingUser = userRepository.findByUsername(registerFormDTO.getUsername());
if (existingUser != null) {
errors.rejectValue("username", "username.alreadyexists", "A user with that username already exists");
model.addAttribute("title", "Register");
return "register";
}
String password = registerFormDTO.getPassword();
String verifyPassword = registerFormDTO.getVerifyPassword();
if (!password.equals(verifyPassword)) {
errors.rejectValue("password", "passwords.mismatch", "Passwords do not match");
model.addAttribute("title", "Register");
return "register";
}
User newUser = new User(registerFormDTO.getUsername(), registerFormDTO.getPassword());
userRepository.save(newUser);
setUserInSession(request.getSession(), newUser);
return "redirect:";
}
|
/register that takes a valid RegisterFormDTO object, associated errors, and a Model. In addition, the method needs an HttpServletRequest object. This object represents the incoming request, and will be provided by Spring.errors object and return the user to the form. See the note on using errors.rejectValue below.Note
The Errors class we have been using in conjunction with model binding will always contain information about errors related to validation annotations on the given model. However, it can also be used to manually generate additional errors. In the method above, we call:
errors.rejectValue("username", "username.alreadyexists",
"A user with that username already exists");
errors.rejectValue takes three parameters:
This is a good time to test your application. Start it up, navigate to /register and try to create a user. If everything goes well, you will see a new row in the user table of the database.
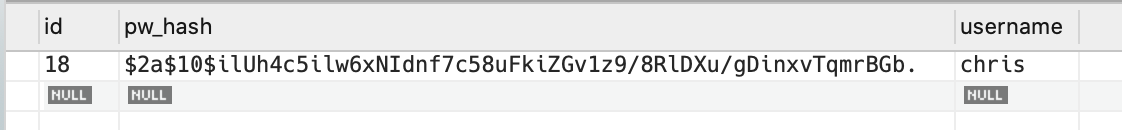
A new row in the user table¶
Rendering the login form is similar to rendering the registration form:
89 90 91 92 93 94 | @GetMapping("/login")
public String displayLoginForm(Model model) {
model.addAttribute(new LoginFormDTO());
model.addAttribute("title", "Log In");
return "login";
}
|
The form template itself should be placed in templates/login.html, and is
also similar to the registration template:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org/">
<head th:replace="fragments :: head"></head>
<body class="container">
<header th:replace="fragments :: header"></header>
<form method="post">
<div class="form-group">
<label th:for="username">Username
<input class="form-control" th:field="${loginFormDTO.username}">
</label>
<p class="error" th:errors="${loginFormDTO.username}"></p>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>Password
<input class="form-control" th:field="${loginFormDTO.password}" type="password">
</label>
<p class="error" th:errors="${loginFormDTO.password}"></p>
</div>
<input type="submit" class="btn btn-primary" value="Log In" />
</form>
<p>Don't have an account? <a href="/register">Register for one.</a></p>
</body>
</html>
As usual, processing the form is more complicated. Again, we’ll break it down in detail.
96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 | @PostMapping("/login")
public String processLoginForm(@ModelAttribute @Valid LoginFormDTO loginFormDTO,
Errors errors, HttpServletRequest request,
Model model) {
if (errors.hasErrors()) {
model.addAttribute("title", "Log In");
return "login";
}
User theUser = userRepository.findByUsername(loginFormDTO.getUsername());
if (theUser == null) {
errors.rejectValue("username", "user.invalid", "The given username does not exist");
model.addAttribute("title", "Log In");
return "login";
}
String password = loginFormDTO.getPassword();
if (!theUser.isMatchingPassword(password)) {
errors.rejectValue("password", "password.invalid", "Invalid password");
model.addAttribute("title", "Log In");
return "login";
}
setUserInSession(request.getSession(), theUser);
return "redirect:";
}
|
POST handler above.User object with the given password from the database.User.isMatchingPassword() method, which handles the details associated with checking hashed passwords.Now you can test your login form. Upon successful form submission, you should be redirected to the home page. To verify that a session was created, open Firefox’s developer tools and navigate to the Storage pane. Select Cookies > http://localhost:8080 in the left-hand pane and you should see a cookie with the key JSESSIONID. This is the session cookie created by the application. (You may see other cookies as well, which is okay.)
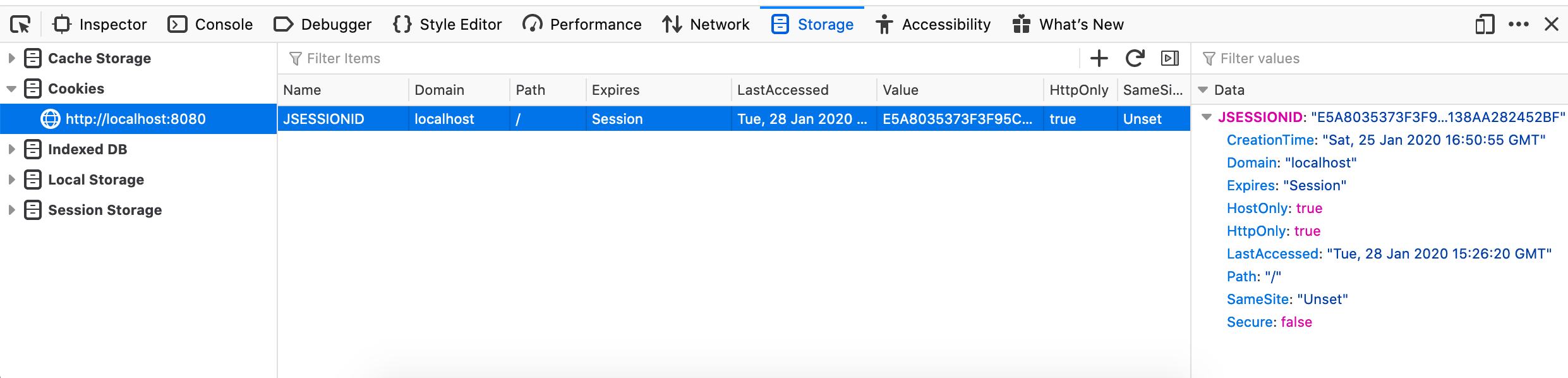
A session cookie for our application¶
After the complicated processes of user registration and login, logging a user out is refreshingly simple.
127 128 129 130 131 | @GetMapping("/logout")
public String logout(HttpServletRequest request){
request.getSession().invalidate();
return "redirect:/login";
}
|
To log out, we simply invalidate the session associated with the given user. This removes all data from the session, so that when the user makes a subsequent request, they will be forced to log in again.
Note
The code for this section is available in the
login-reg-forms branch
of the coding-events-demo repository.
Question
What is the name of the new method we have introduced on the Errors object?
Errors.hasErrors()Errors.errors()Errors.isNotEmpty()Errors.rejectValue()Question
Which developer tool panel can we use to verify that a user session has been started?