Inheritance¶
Object-oriented programming is a type of software design where the codebase is organized around objects and classes. Objects contain the functions and central logic of a program.
Object-oriented programming stands on top of four principles: abstraction, polymorphism, encapsulation, and inheritance. We will dive into inheritance now.
Inheritance refers to the ability of one class to acquire properties and methods from another.
Think of it this way, in the animal kingdom, a species is a unique entity that inherits traits from its genus. The genus also has unique properties, but inherits traits from its family. For example, a tiger and a housecat are members of two different species, however, they share similar traits such as retractable claws. The two cats inherited their similar traits from their shared family, felidae.
Using inheritance in programming, we can create a structure of classes that inherit properties and methods from other classes.
If we wanted to program classes for our tiger and housecat, we would create a felidae class for the family. We would then create two classes for the panthera genus and the felis genus. We would create classes for the tiger and house cat species as well. The species classes would inherit properties and methods from the genus classes and the genus classes would inherit properties and methods from the family class.
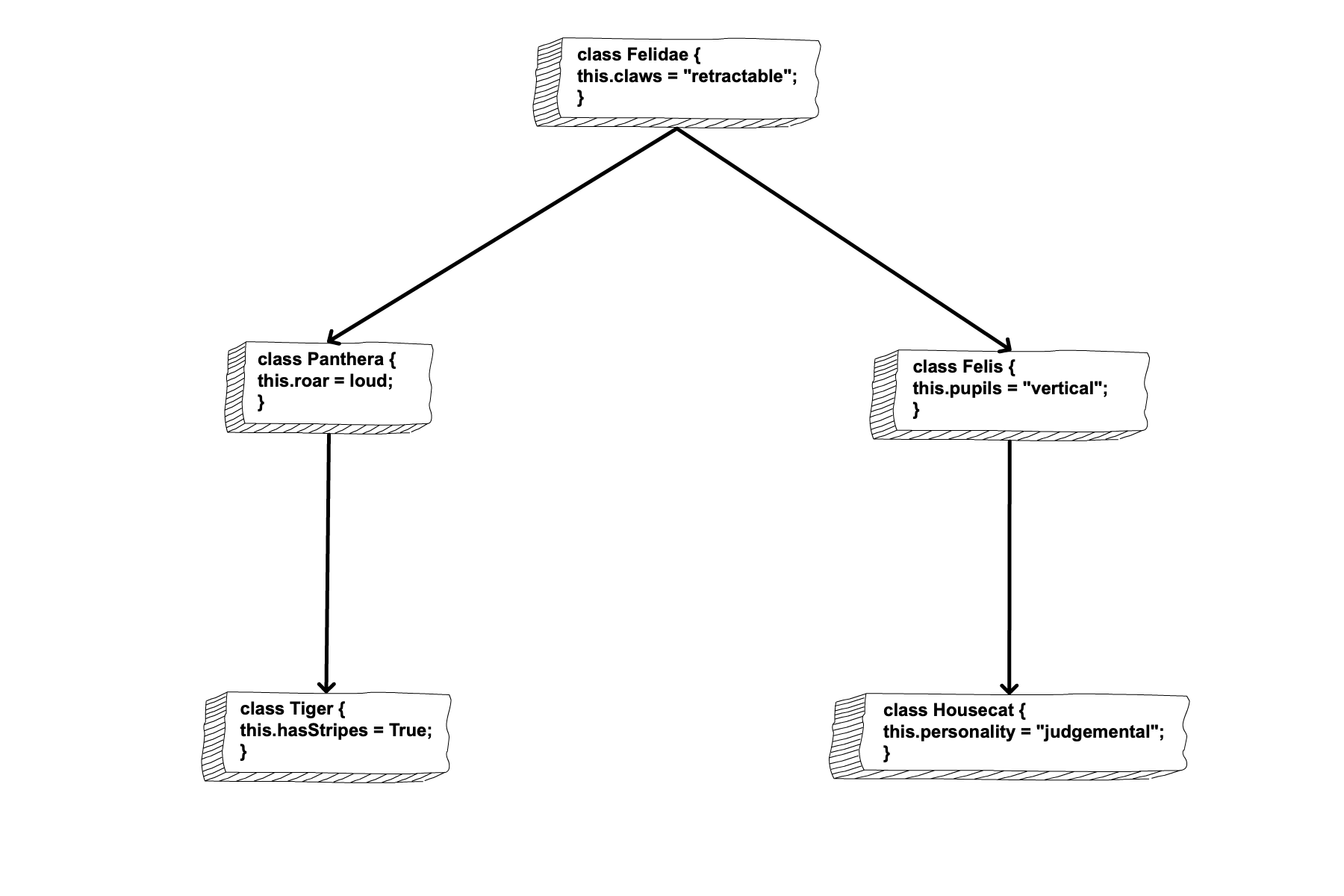
The classes inheriting properties and methods are child classes, and the classes passing down properties and methods are parent classes.
