UNION, INTERSECT, EXCEPT
UNION
Note
The following examples will reference the tables Movies and More_Movies. You can view the data for them here: Movies and More_Movies table data
The UNION operator combines table rows from multiple query statements. This is especially useful if you would like to view data from multiple tables without including duplicates. By default, the UNION set operator will return data without duplicates. However, if you wish to include duplicates in your returned data you can do so by using the ALL keyword with UNION.
Example
-- Select all data from the Movies Table
SELECT * FROM Movies
-- Apply the UNION set operator to concatenate the two SELECT queries into a single result
UNION
-- Select all data from the More_Movies Table
SELECT * From More_Movies
GOThe above code will return a result set of data from the Movies and More_Movies tables with only unique rows (no duplicates).
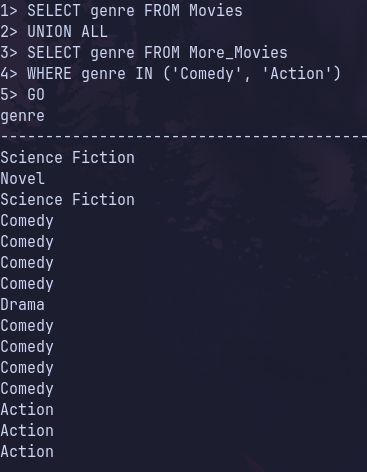
SELECT * genre FROM Movies
-- Apply the UNION ALL set operator to include all data from both Movies and More_Movies tables
UNION ALL
SELECT * genre FROM More_Movies
-- where clause to include only the comedy and action genres in the union
WHERE genre IN ('Comedy', 'Action')
GOThe above code using the ALL keyword will return a result set of data including all genres from the Movies table, and only the comedy and action genres from the More_Movies table (duplicates included).
The UNION operator does not require multiple tables in order to work. It is also useful for returning a set of data with only unique rows when working on the same table but with mutliple query statements.
Example
SELECT * FROM Movies
WHERE genre = 'Science Fiction'
UNION
SELECT * FROM Movies
WHERE genre = 'Comedy'
GOThe above code will return a result set of data from the Movies table that are in the Science Fiction and Comedy genre, without providing any duplicates.
INTERSECT
The INTERSECT set operator differs from UNION in that it will only return commonalities among rows from your queries instead of concatenating the result sets together. Similar UNION, the INTERSECT set operator will not return any duplicate values in the result set.
Example
The two examples below will compare the results from an INTERSECT and UNION set operator using the same queries.
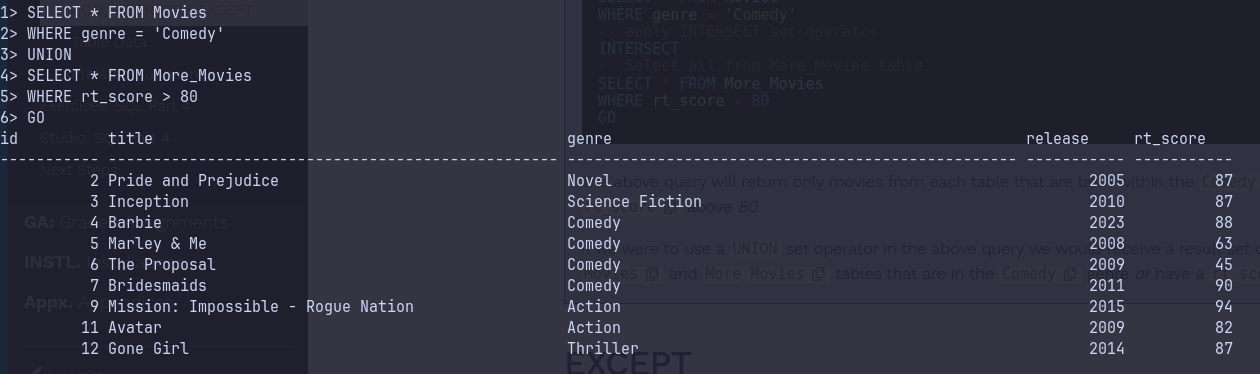
-- Select all from Movies table
SELECT * FROM Movies
WHERE genre = 'Comedy'
-- apply INTERSECT set operator
INTERSECT
-- Select all from More_Movies table
SELECT * FROM More_Movies
WHERE rt_score > 80
GOResult
The above query will return only movies from each table that are both within the Comedy genre and have a rt_score above 80.
If we were to use a UNION set operator in the above query we would receive a result set of all movies within the Movies and More_Movies tables that are in the Comedy genre or have a rt_score above 80:
SELECT * FROM Movies
WHERE genre = 'Comedy'
UNION
SELECT * FROM More_Movies
WHERE rt_score > 80
GOResult
EXCEPT
The EXCEPT operator acts as a a separator between the left and right query in that it will return a result of rows that meet the criteria of the left query but not the right. Similar to both the INTERSECT and UNION set operators it will only return unique values, removing any duplicates present by default.
Example
Check Your Understanding
Question
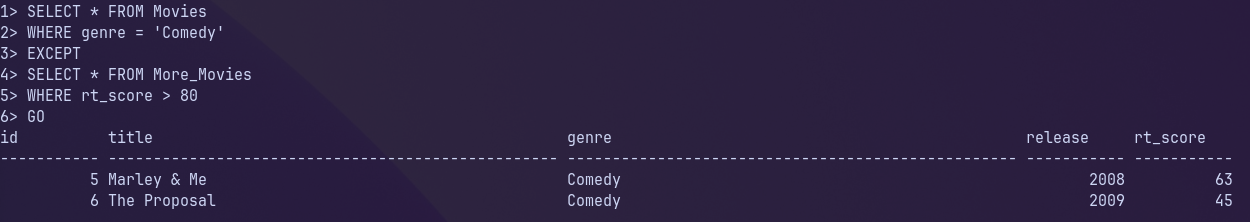
What would be the result of the following query?
SELECT * FROM Movies
WHERE genre = 'Comedy'
EXCEPT
SELECT * FROM More_Movies
WHERE genre = 'Comedy'
GO