Installing Jupyter Notebook
Setting up Jupyter Notebook
Jupyter is a non-profit, open-source project that offers various tools and solutions. This course will utilize Jupyter Notebook for documentation and code editing all within your browser.
Note
This course will have you install python packages in your global environment.
The following commands will install Jupyter Notebook in your global environment:
pip install notebook
Warning
If the above command produces an error you may need to specify pip3 like so:
pip3 install notebook
Note
pip is a package manager that is included with any Python installation. You can verify the version and installation of pip by typing in the following command:
Unix/MacOS:
python3 -m pip --version
Windows:
py -m pip --version
Start the App Server
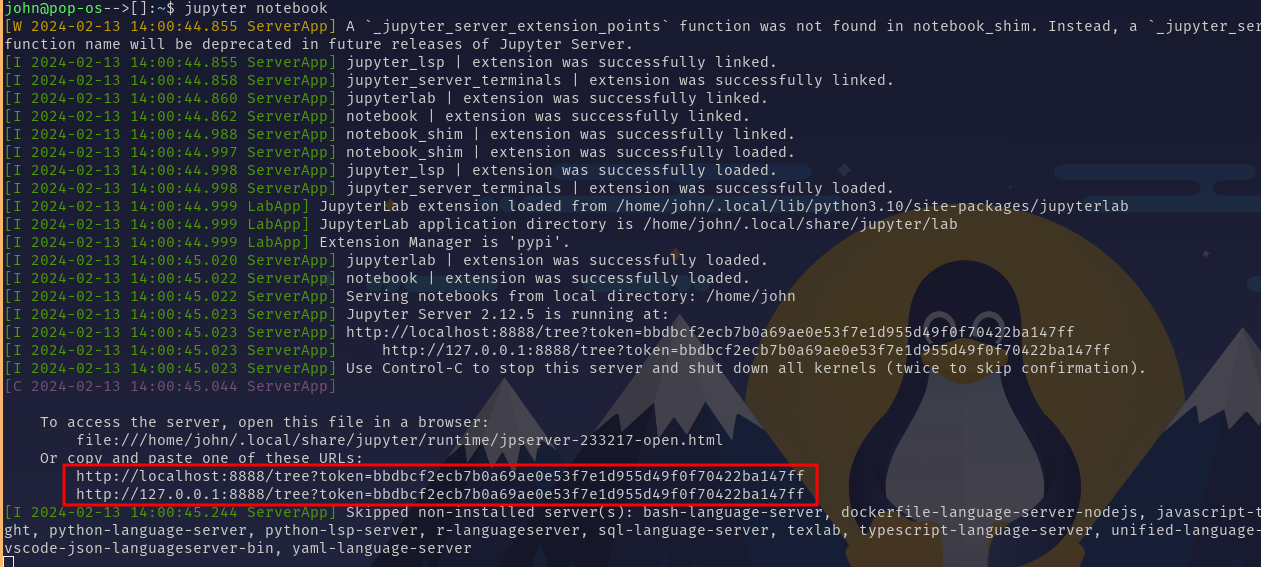
Open Jupyter Notebook with the following command:
jupyter notebook
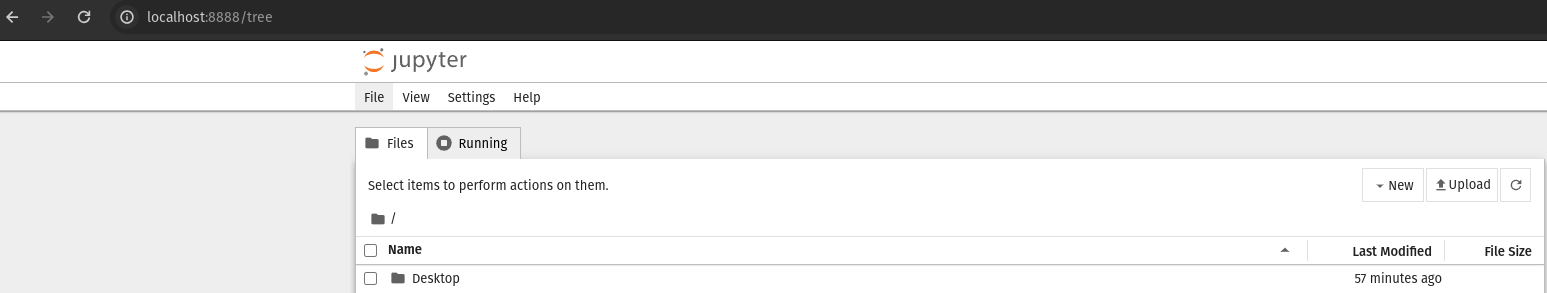
Verification
The running application will look similar to the image below:
Note
If a browser window with a running Jupyter notebook application does not happen automatically, you can copy and paste one of the highlighted links into the browser of your choice.