pandas DataFrames
A pandas DataFrame is the second type of class that is capable of handling data.
Similar to a spreadsheet, a DataFrame can be visualized as having multiple columns and rows associated with the data inside. The data within can be of any type.
A DataFrame can also be considered a collection or assortment of Series. Similar to a Series there are multiple ways that a DataFrame can be created:
- Using a multi-dimensional list, dictionary, or tuple
- Combining or joining multiple Series together
- From a pre-existing CSV file
Note
The examples above are not the only options you have for creating a DataFrame but they are the ones we will focus on in this section.
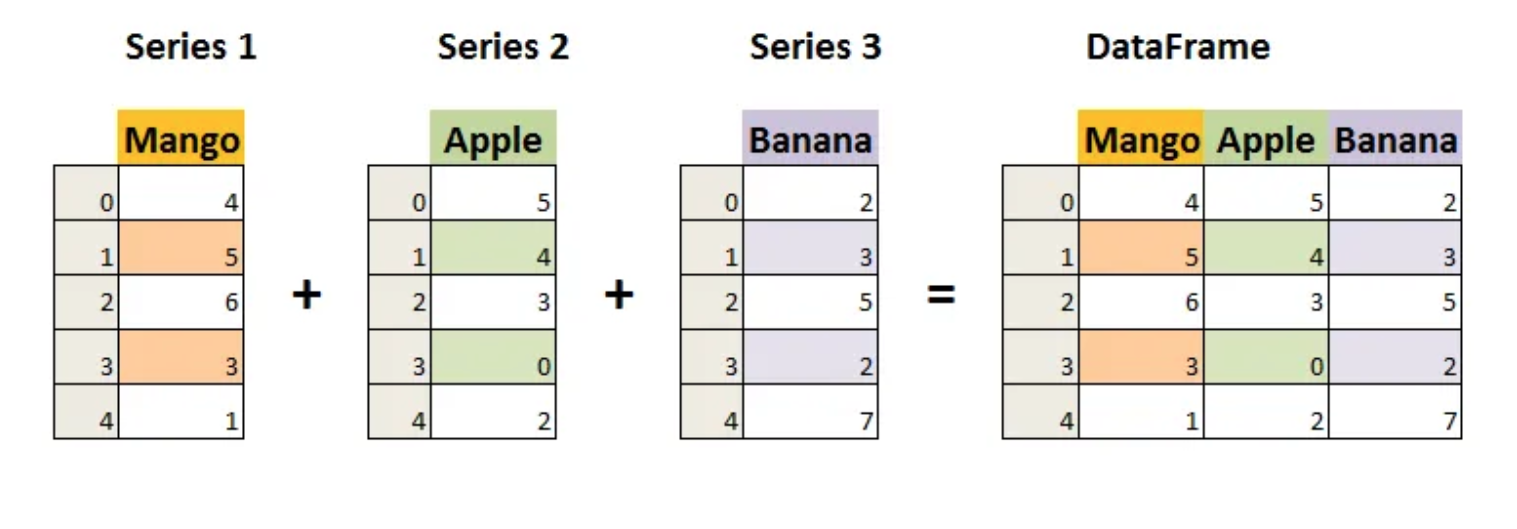
Column values within a DataFrame are referred to as a Series. Below is an example of how multiple Series might be used to build a DataFrame
The image below provides another visual of the general DataFrame structure. A DataFrame is similar to a Python dictionary in that the column names are like keys and the values are the data for that column.

Creating a DataFrame
Let’s dive in to some different ways you can create a DataFrame.
Using a Multi-Dimensional List
| |
The above code block accomplishes the following:
- imports pandas.
- Creates a pandas DataFrame called
movie_list_of_listsby providing a list of lists as a parameter into the.DataFrame()function.. - Creates a pandas DataFrame called
dataframe_from_existing_listby using the already existing listmovies_dataframe_dataand passing it in as a parameter to the.DataFrame()function.
Note
One thing to note about lists when they are added into a DataFrame is that each list represents a row not a column.
Using a Dictionary
| |
The above code block accomplishes the following:
- imports pandas.
- Creates a pandas DataFrame called
movie_dictionary_dataframeby providing a dictionary as a parameter to the.DataFrame()function. - Creates a pandas DataFrame called
dataframe_from_movies_dictionaryby using the already existing dictionarymoviesand passing it in as a parameter to the.DataFrame()function.
Using a Tuple
| |
The above code block accomplishes the following:
- imports pandas.
- Creates a pandas DataFrame called
movies_tuple_dataframeby providing a tuple as a parameter to the.DataFrame()function. - Creates a pandas DataFrame called
dataframe_from_existing_tupleby using an already existing tuplemovies_dataand passing it in as a parameter to the.DataFrame()function.
Creating a DataFrame from Series
In the following example we will create a DataFrame from two Series using pandas and the .concat() function included with the pandas library.
Example
| |
Output
movies genres
1 Interstellar Science Fiction
2 Pride and Prejudice Novel
3 Inception Science Fiction
4 Barbie Comedy
Note
the axis parameter specifies whether the data will be joined or combined along the row or column. Take a look at the table below. If you do not specify axis=1 it will default to axis=0.
| Axis | Represents | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| 0 (default) | Row | Operations performed across rows |
| 1 | Column | Operations performed down each column |
Column Data
Suppose you want to view data from one particular column or compare specific columns to one another. You can do so by using the column labels to pull them aside. Let’s take a look at how to do so using the same dictionary we created above.
Example
# import pandas
import pandas as pd
movies = {'Name': ["Interstellar", "Pride and Prejudice", "Inception", "Barbie"],'Release': [2014, 2005, 2010, 2003]}
movies_dataframe = pd.DataFrame(movies)
movie_names = movies_dataframe["Name"]The above example accomplishes the following:
- Imports pandas
- Creates a dictionary called
movieswith the columnsNameandRelease. - Creates a DataFrame from the
moviesdictionary - A new variable called
movie_namesis created to store the values within theNamecolumn of themovies_dataframe.
Multiple Column Data
Now that you have seen how to pull aside a single column’s data let’s take a look at how to grab multiple columns and store them inside of a variable.
Example
# import pandas
import pandas as pd
movies = {'Name': ["Interstellar", "Pride and Prejudice", "Inception", "Barbie"],'Release': [2014, 2005, 2010, 2023], 'Genre': ["Science Fiction", "Novel", "Science Fiction", "Comedy"]}
movies_dataframe = pd.DataFrame(movies)
# Pull aside the Name and Genre columns from the movies_dataframe
movie_names_and_genres = movies_dataframe[["Name", "Genre"]]Note
Since we are grabbing specific columns from an already existing DataFrame and there are no joins happening we do not need to specify an axis.
Check Your Understanding
Question
True or False: Column names cannot be changed in a DataFrame.
Question
True or False: A DataFrame column is a Series.